INAV T-tail Layout Fixed-wing Tuning Guide
This tutorial is based on INAV firmware version 7.0.0; operations may vary slightly with other firmware versions.
Some content references the SpeedyBee APP interface and is consistent with INAV configurator settings.
Parameter tuning can be performed using either the SpeedyBee APP or the INAV configurator.
I. Introduction to Flight Principles
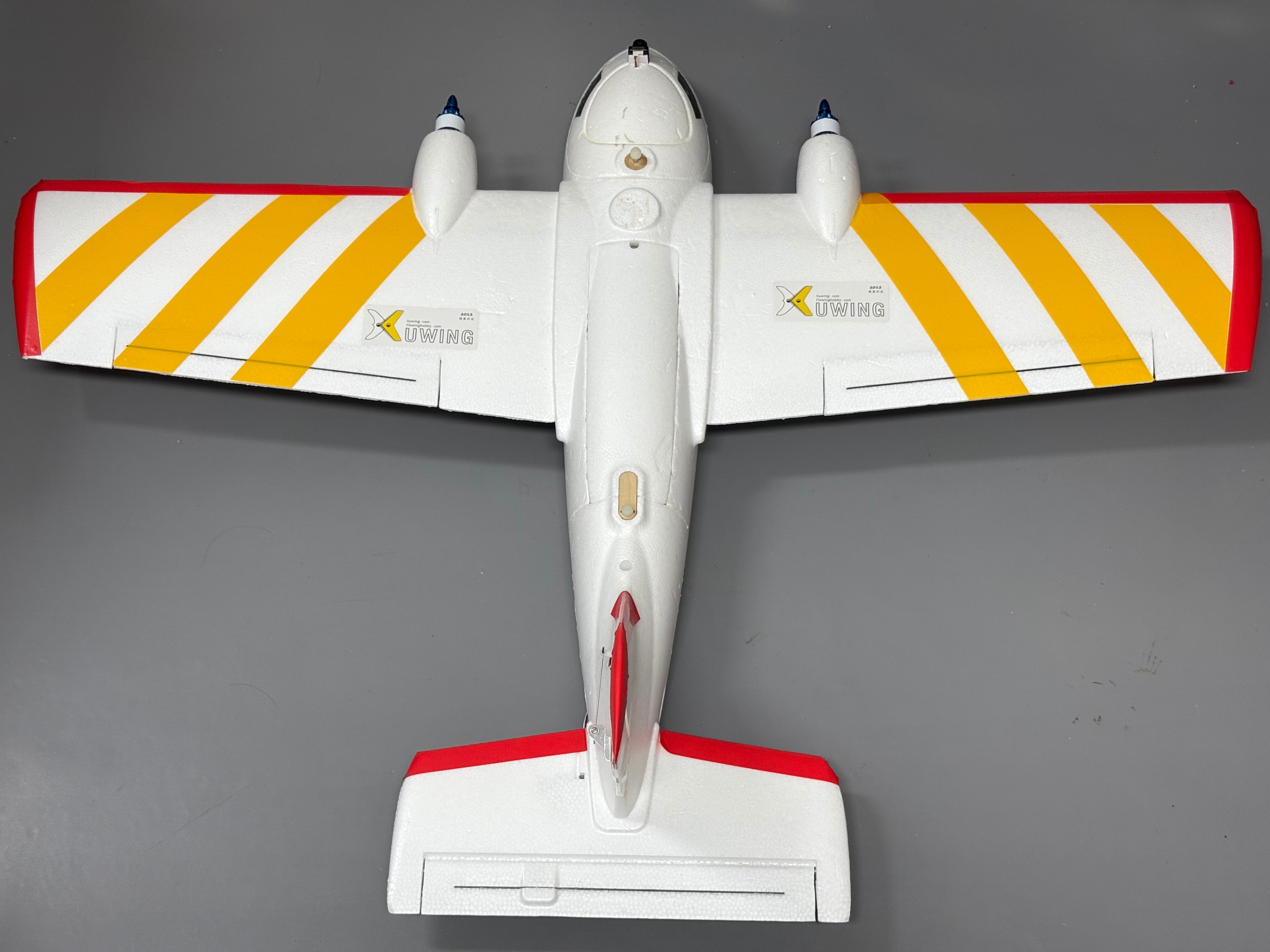
The inverted T-tail (Conventional Tail) is one of the most common tail configurations for fixed-wing airplane, consisting of a Horizontal Stabilizer and a Vertical Stabilizer. Its distinguishing feature is that the Horizontal Stabilizer is installed at the rear of the fuselage, lower than the main wing, while the Vertical Stabilizer is centrally positioned, forming an inverted "T" structure.
The design of the inverted T-tail positions the horizontal stabilizer below the fuselage. Compared to a conventional T-tail, it interacts more directly with airflow, leading to the following characteristics:
- Reduced dependence on angle-of-attack: airflow can act more consistently on the tail, reducing stall risks at high angles of attack.
- More direct pitch control: with the horizontal stabilizer closer to the airflow from the main wing, elevator responses are more immediate and control feels more linear.
- Improved wind resistance: compared to the higher-positioned T-tail layout, the low-mounted stabilizer experiences less interference from crosswinds, offering greater stability during landing.

II. Equipment Preparation
Essential Equipment:
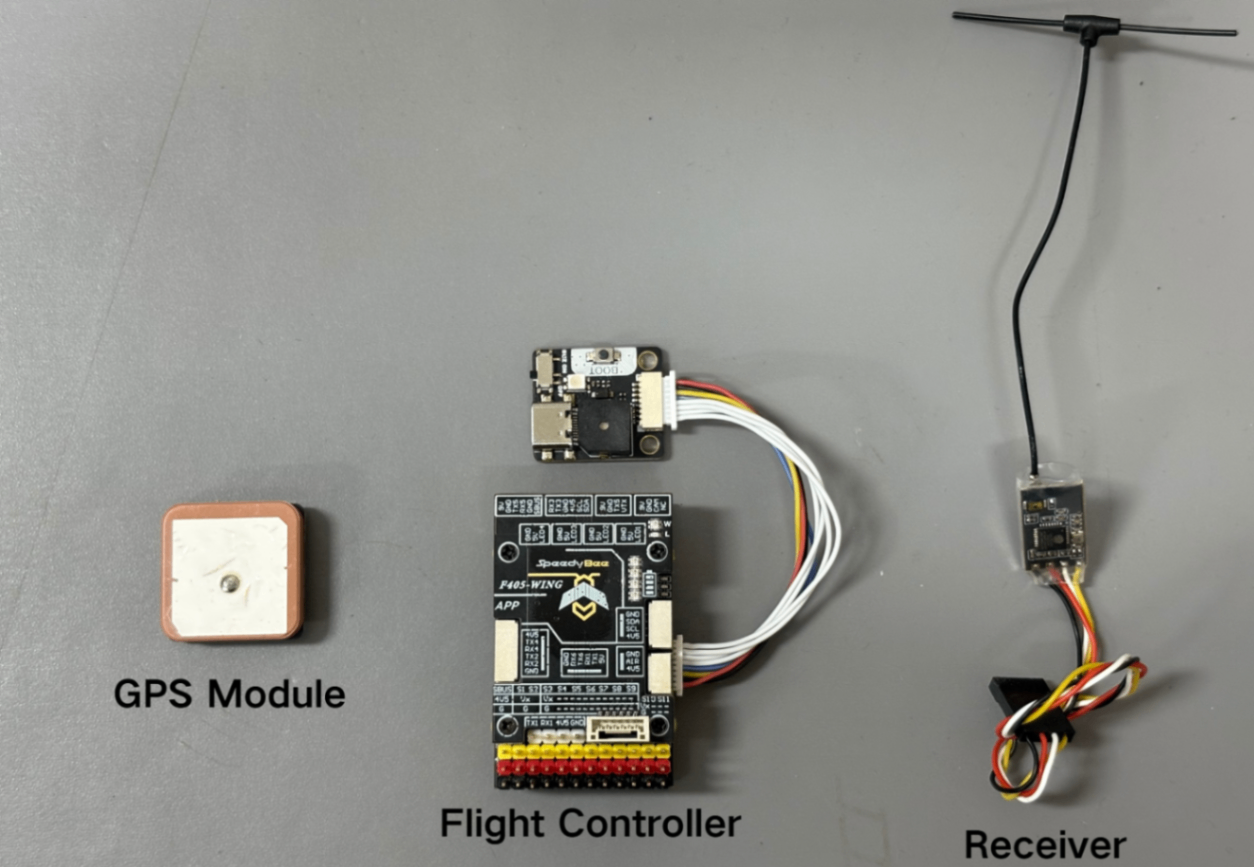
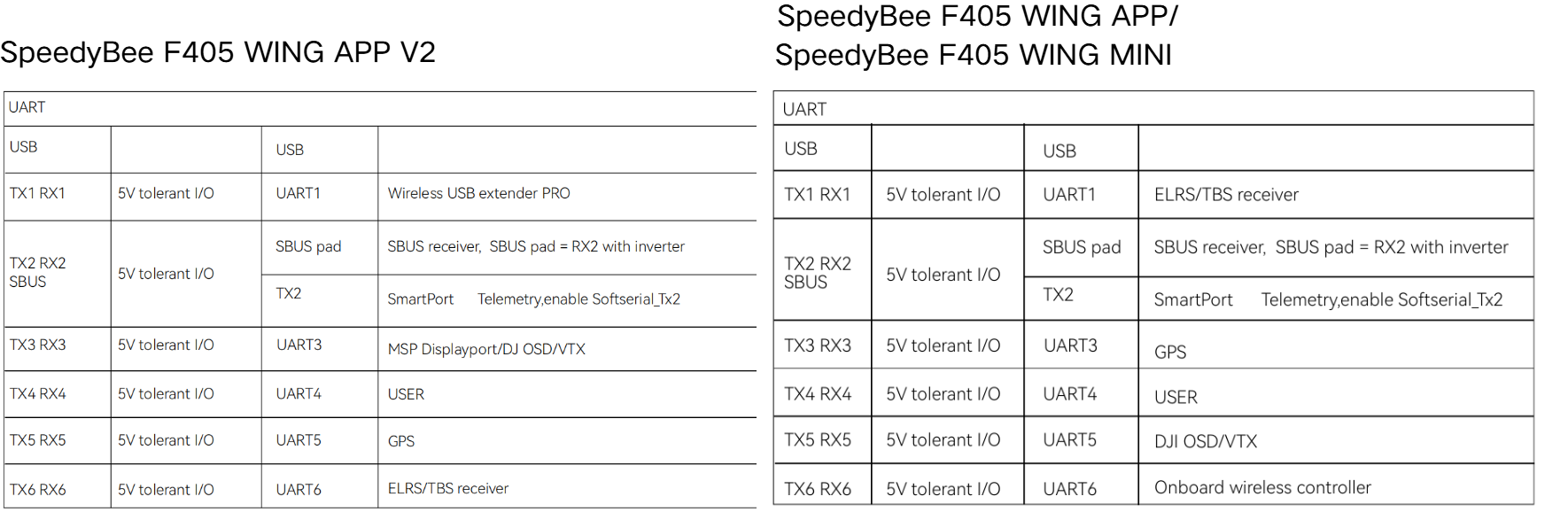
1) Flight Controller: This tutorial is applicable to any of the following models: SpeedyBee F405 WING APP / SpeedyBee F405 WING MINI / SpeedyBee F405 WING APP V2.
2) Radio Controller: Illustrated using RadioMaster Boxer / RadioMaster TX16S as examples.
3) Receiver: Illustrated using the SpeedyBee ELRS Nano 2.4G RX as an example.
4) GPS Module: Illustrated using the BZ-251 GPS module as an example.
5) Motor: Original AVIC 2212 KV980 motor, suitable for Finwing, provided for reference only.
6) ESC: 35–45A ESC, suitable for Finwing, provided for reference only.
7) Servo: 12g metal gear servo, suitable for Finwing, provided for reference only.
8) Battery: 6S1P 10000mAh battery, suitable for Finwing, provided for reference only.
9) Propeller: 8-inch two-blade propeller, suitable for Finwing, provided for reference only.
Optional Equipment:
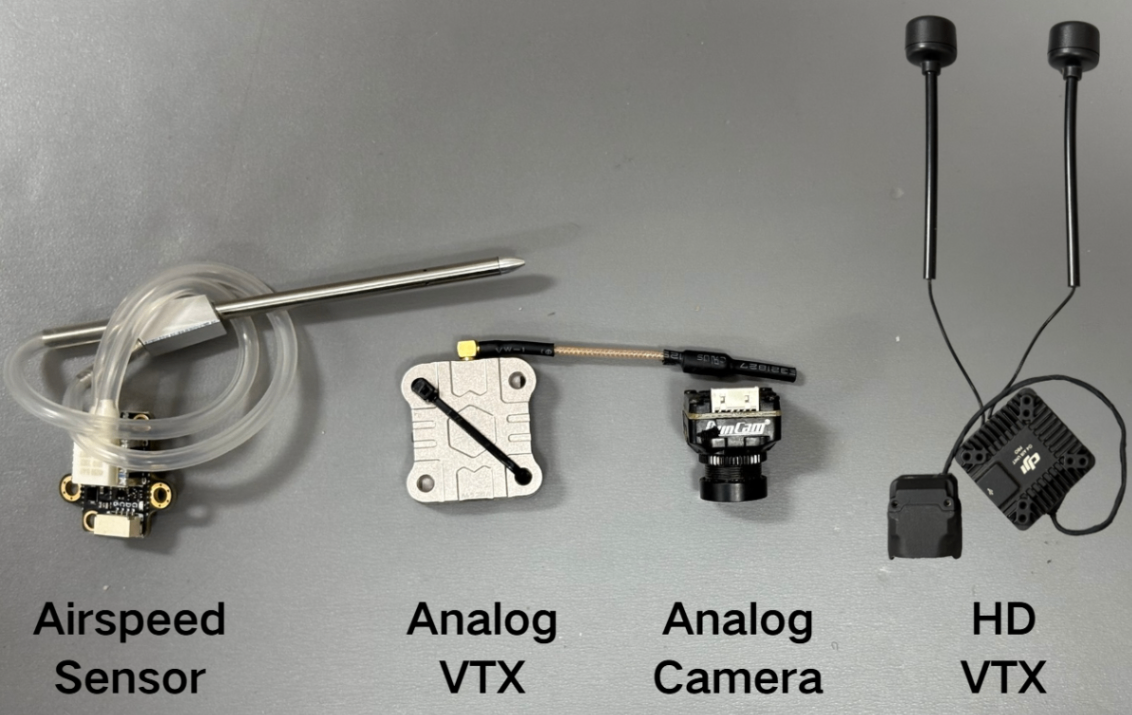
1) Analog VTX: Illustrated using the SpeedyBee TX1600 VTX and RunCam Phoenix2 SE V2 camera as examples.
2) HD VTX: Illustrated using the DJI O4 AIR UNIT as an example.
3) Airspeed Sensor: A digital airspeed sensor is recommended.
For Ground Station Installation, refer to this article: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/software/insoftware/inav-version-install.html How to update flight controller firmware using INAV Ground Station: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/beforetuning/inav-fw-update.html
III. Initial Setup
3.1 Model Configuration
- Connect the Flight Controller to the configurator using a USB data cable.
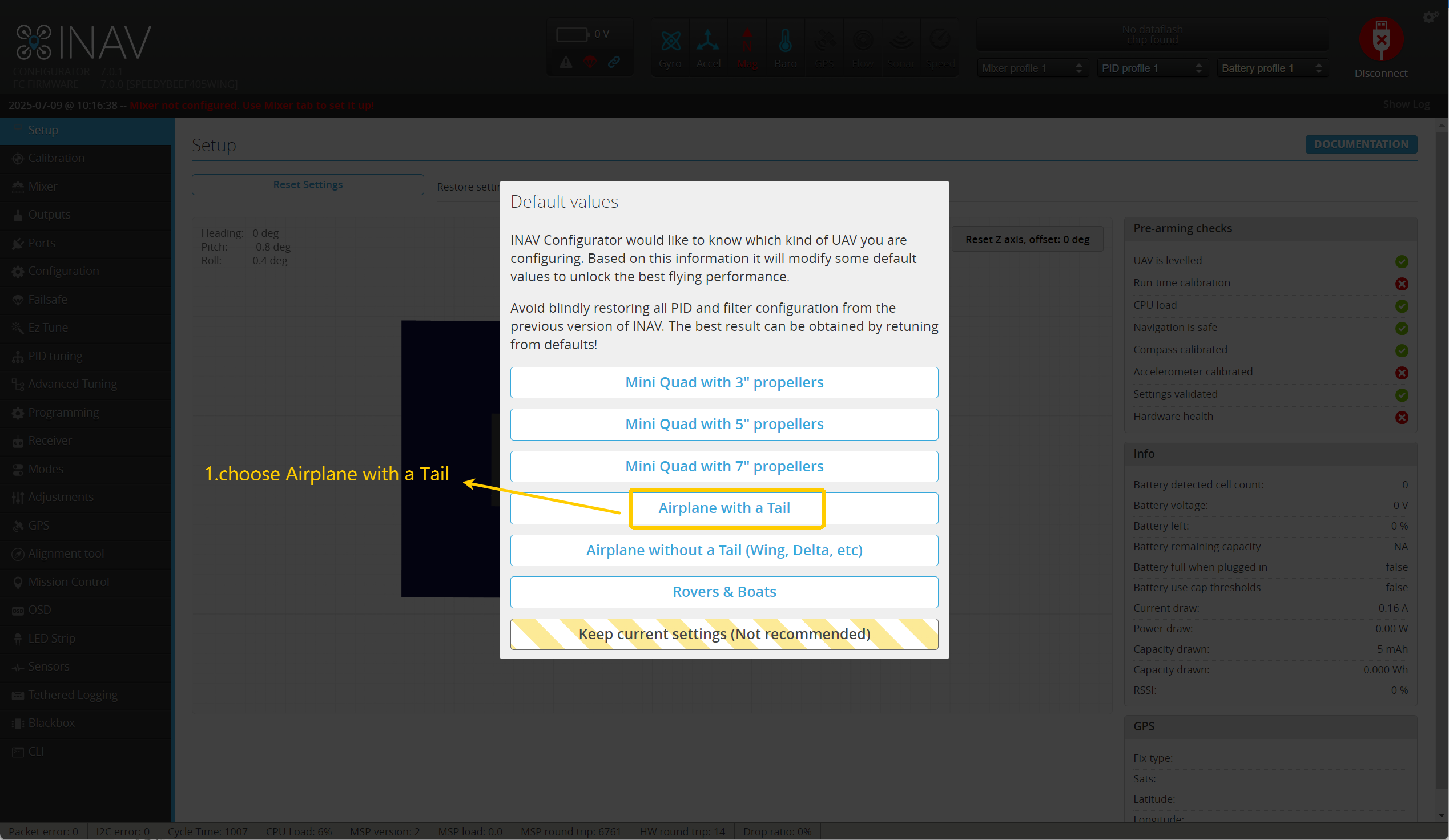
- Open INAV Configurator and click Connect.
If a pop-up appears, select " Airplane with a Tail”.
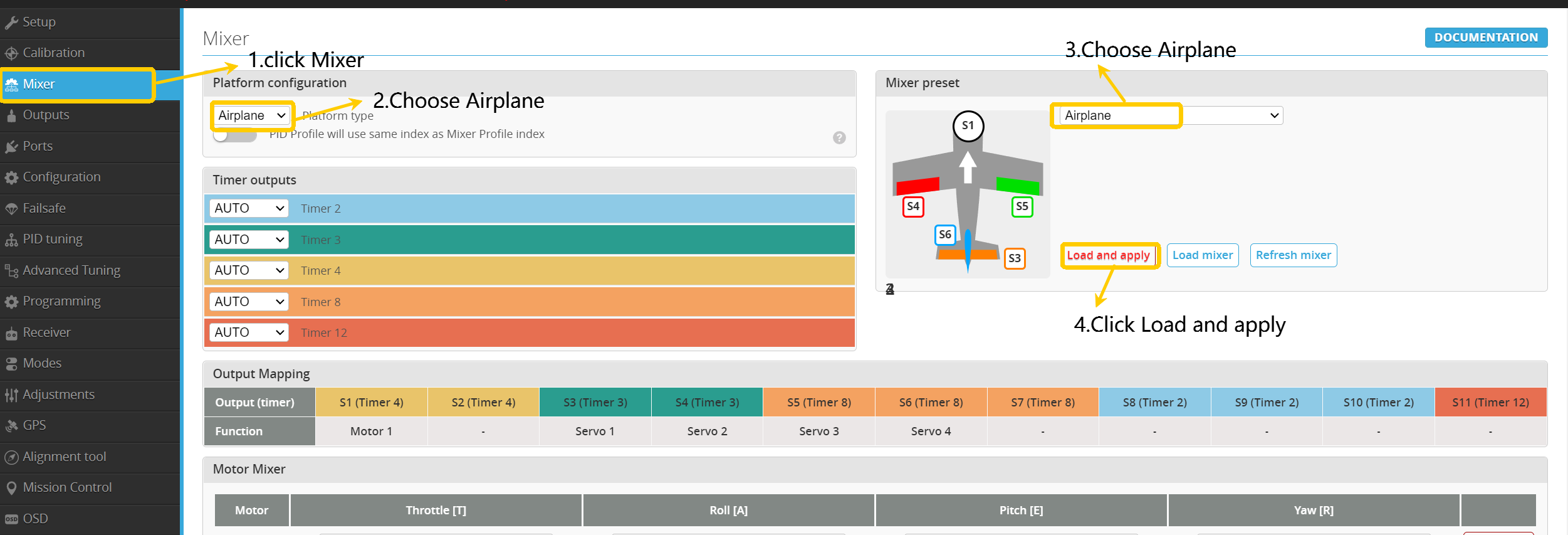
Enter Mixer, select " Airplane”, and click " Load and apply”.
3.2 Accelerometer Calibration
Note: For accurate accelerometer calibration and stable flight, remove the Flight Controller from the airplane and calibrate it on a flat, level surface!
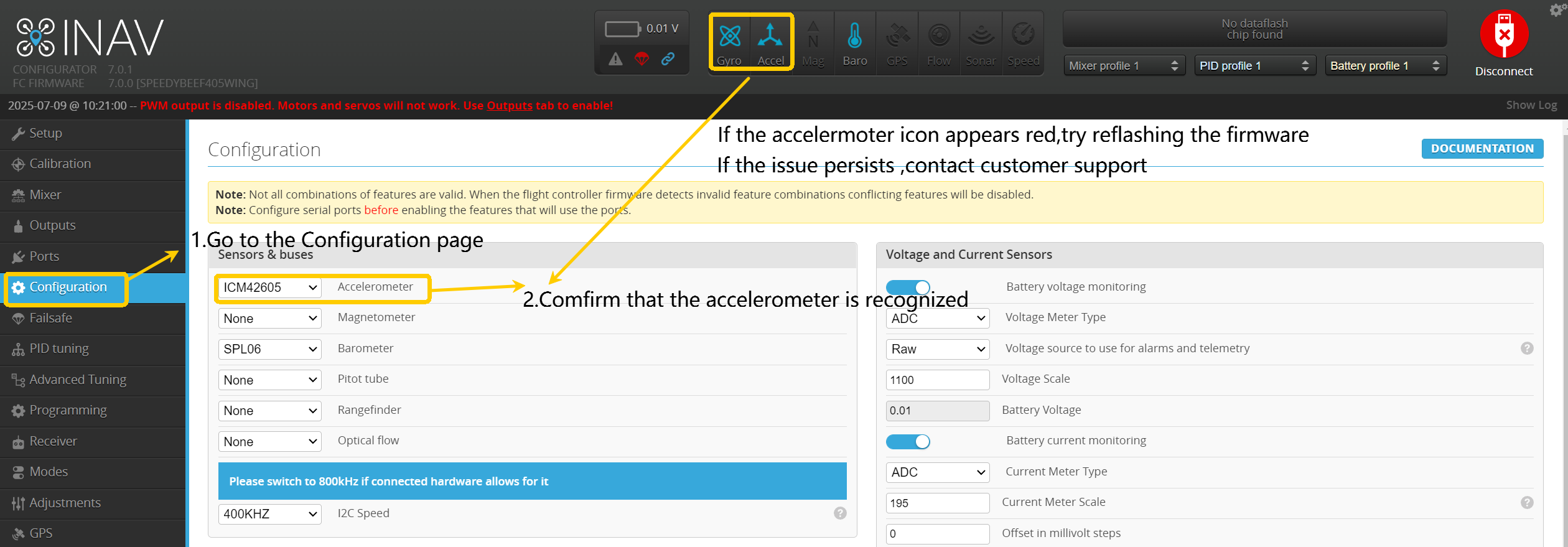
- Enter the Configuration page.
- Select "Auto" to automatically detect and confirm that the accelerometer has been recognized.
If displayed in red, attempt to reflash the firmware; if unresolved, contact after-sales support!
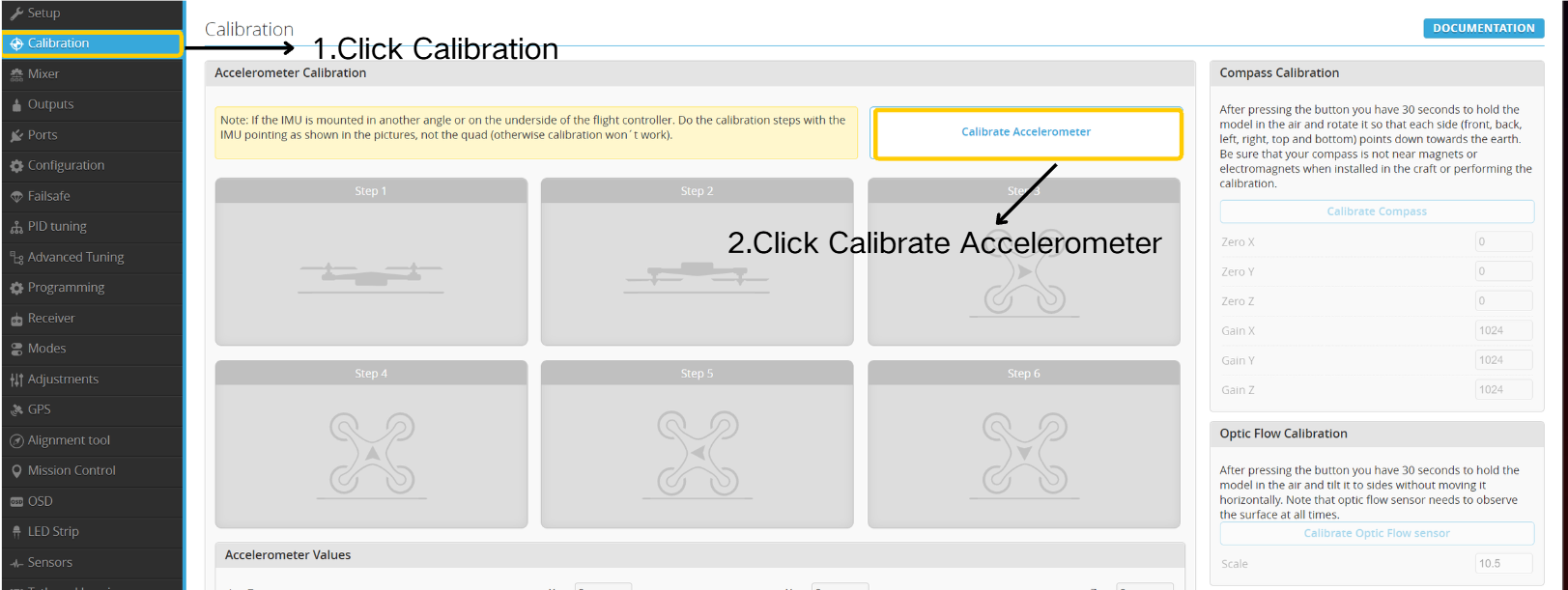
- Click " Calibration”.
- Click " Calibrate Accelerometer”.
- Calibrate according to the illustrated instructions.
Click " Calibrate Accelerometer" once for each orientation calibrated.
The images below correspond directly to the accelerometer calibration steps above.

Click " Save and Reboot" after completing calibration.
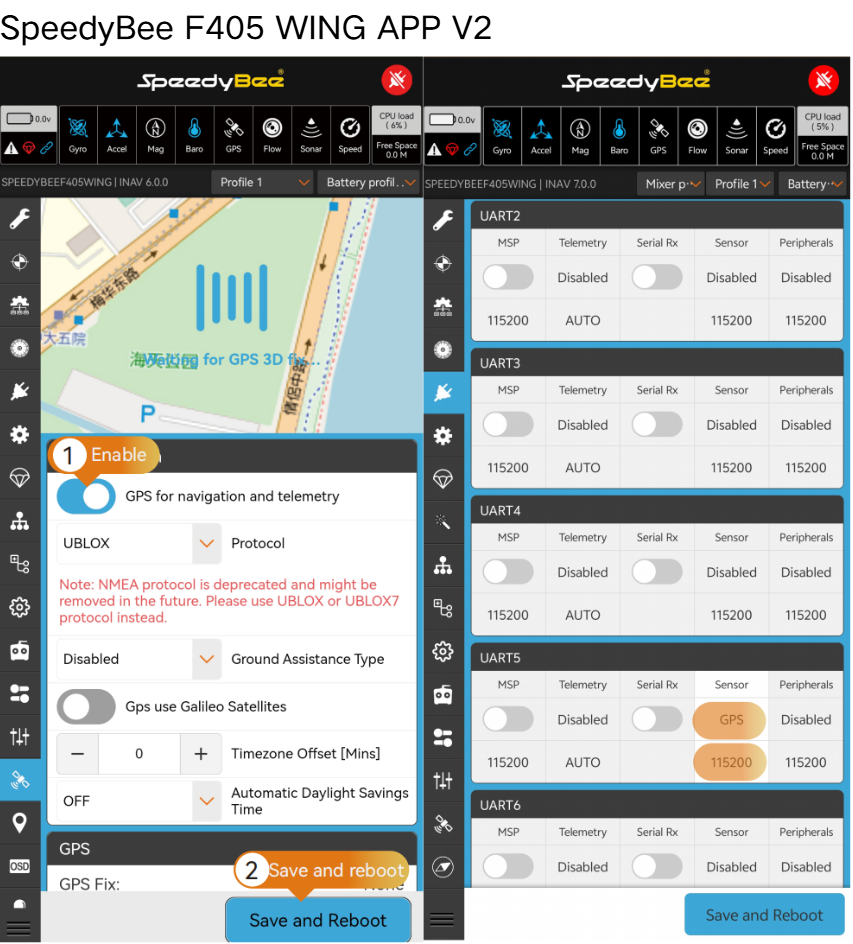
3.3 Port Configuration
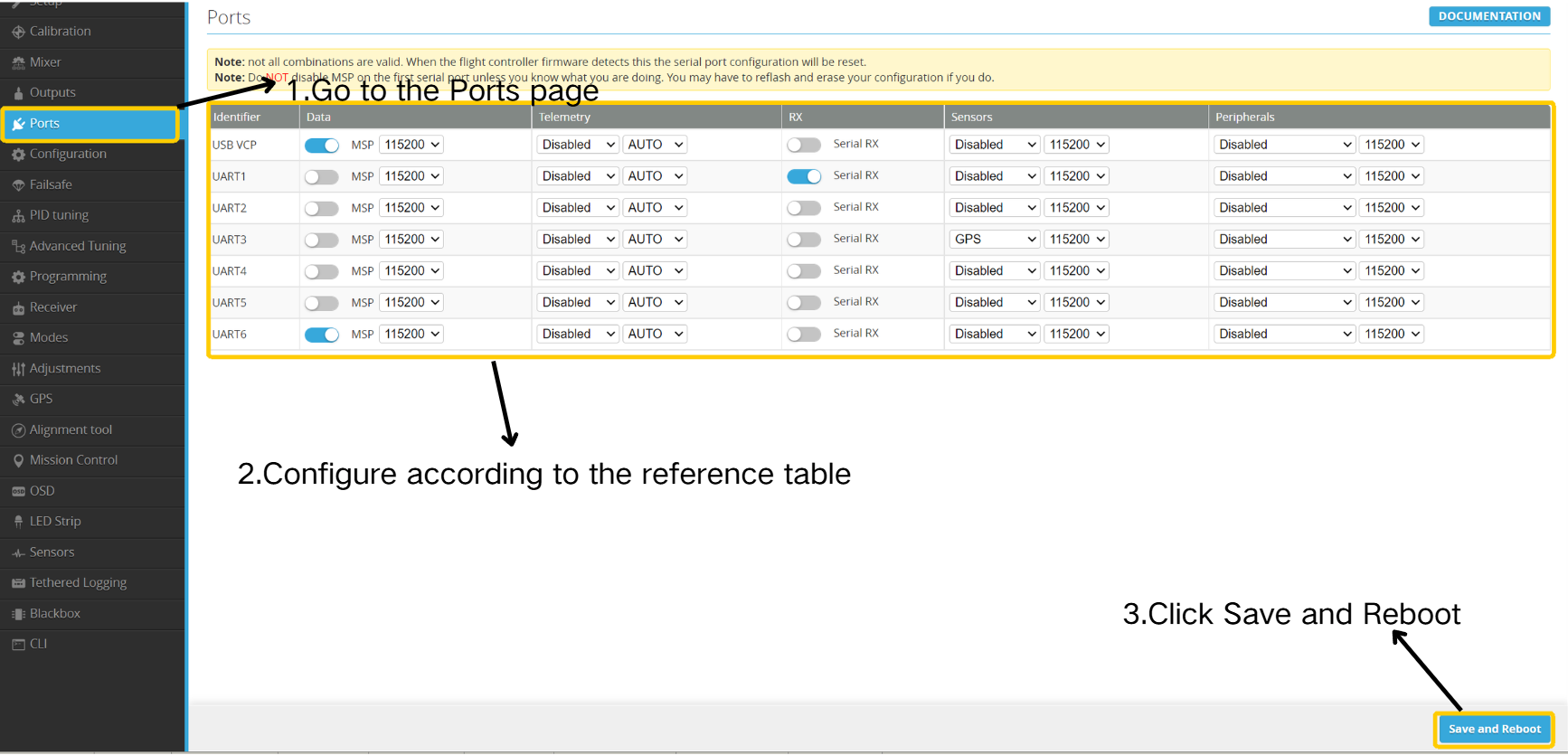
- Enter the Ports page.
- Configure settings according to the reference table.
- Click "Save and Reboot”.
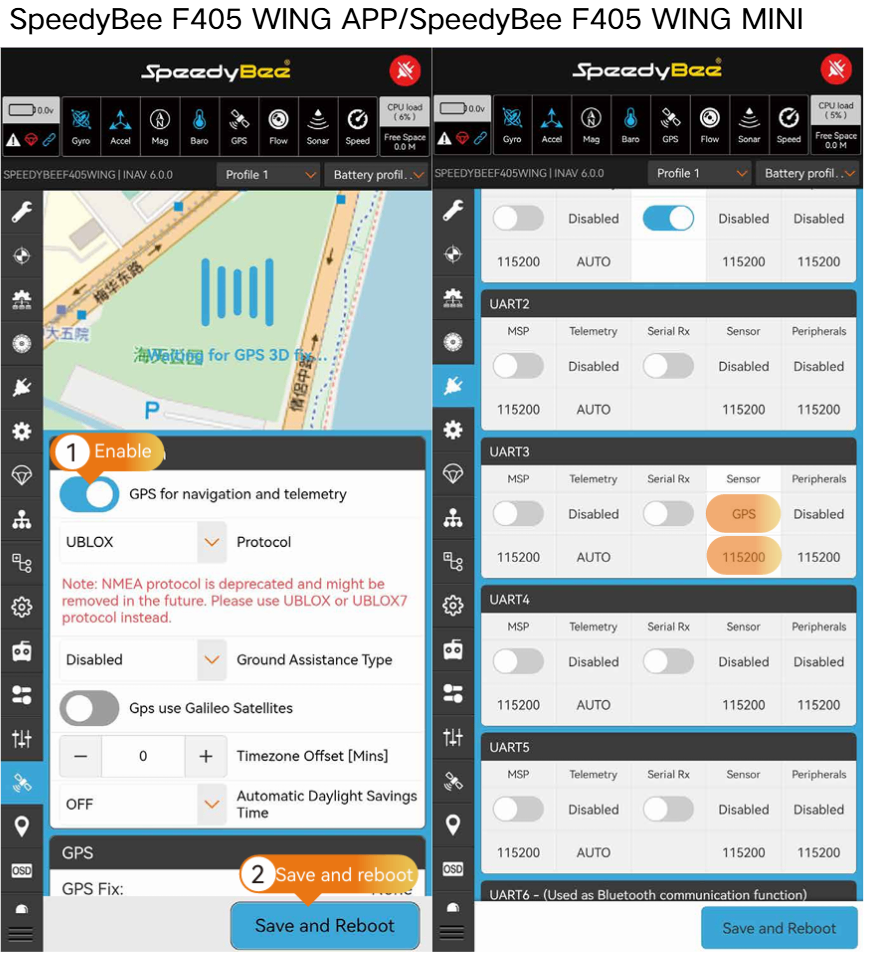
3.4 GPS Configuration
GPS shall be enabled to access NAV RTH (Return-to-Home) flight mode settings on the Modes page.
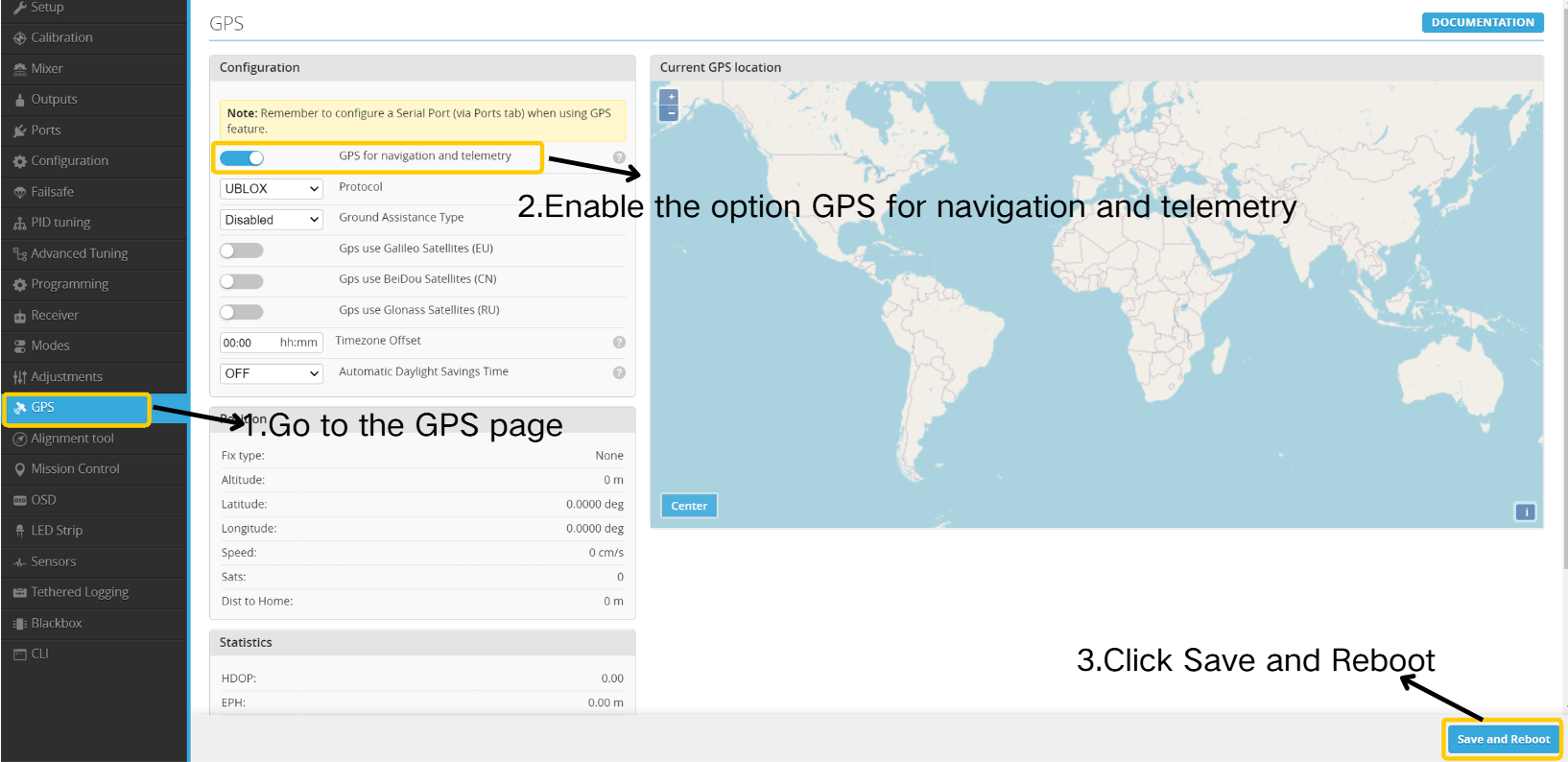
- Enter the GPS page.
- Enable the option " GPS for navigation and telemetry”.
- Click " Save and Reboot”.
3.5 Radio Controller and Flight Mode Configuration
3.5.1 Radio Controller Configuration
1. Bind your radio controller to the receiver before proceeding with the following steps.
2.For details on how to bind an ELRS receiver to the transmitter, refer to this article: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/ardupilot/settings/rc/elrs-bind.html
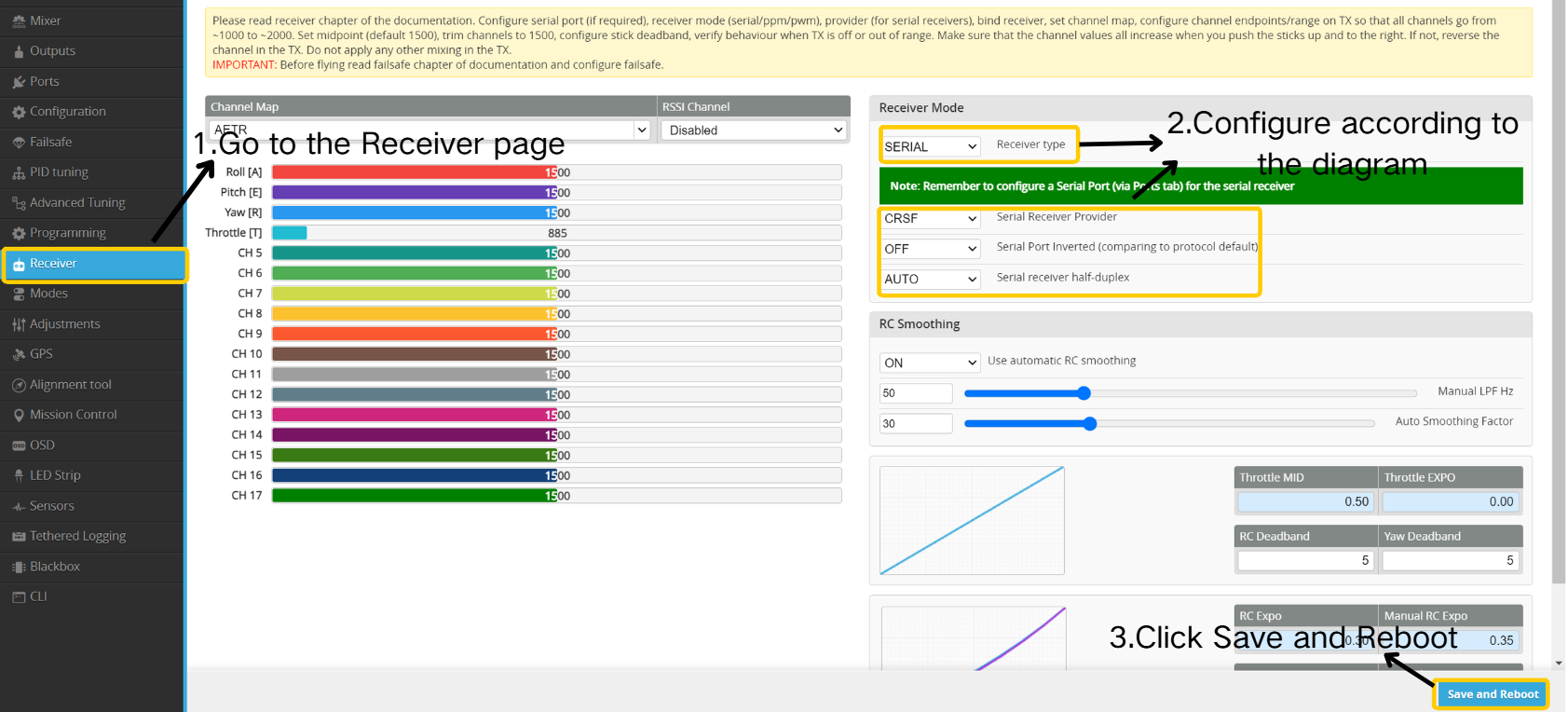
- Navigate to the Receiver page.
- Configure settings according to the illustrated guide.
- Click " Save and Reboot”.
For detailed instructions on how to set channel endpoints in EdgeTX, refer to this article: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/rc/edgetx-endpoint-setup.html
• Navigate to the MDL/MIXES page and ensure CH1–CH4 are configured as illustrated. If not, adjust your radio mixes accordingly.
3.5.2 Arming Channel Setup
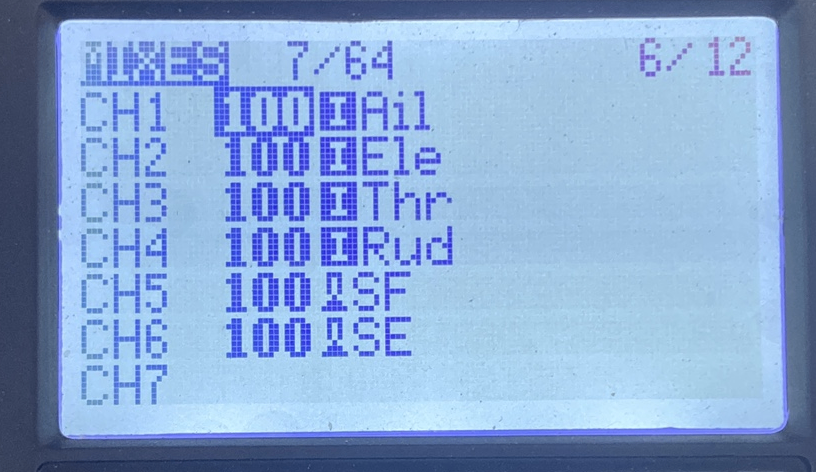
1.Radio Controller Settings
- Select a two-position switch
- Navigate to the MDL / MIXES page and assign it to CH5
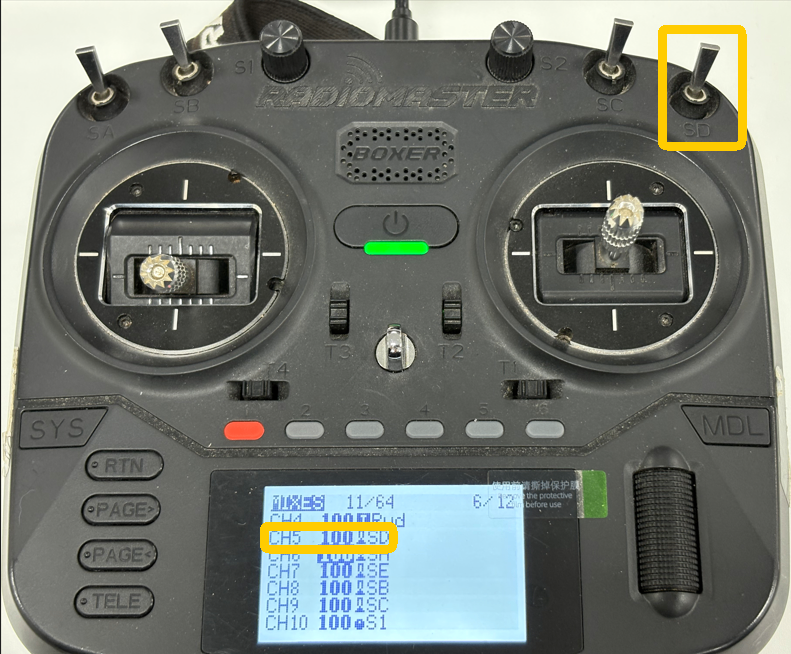

2. Ground Station Setup
⚠️ Note: Arming is only allowed in flight modes that do not require GPS, such as ANGLE . Arming is not possible in GPS-dependent modes like NAV ALTHOLD.
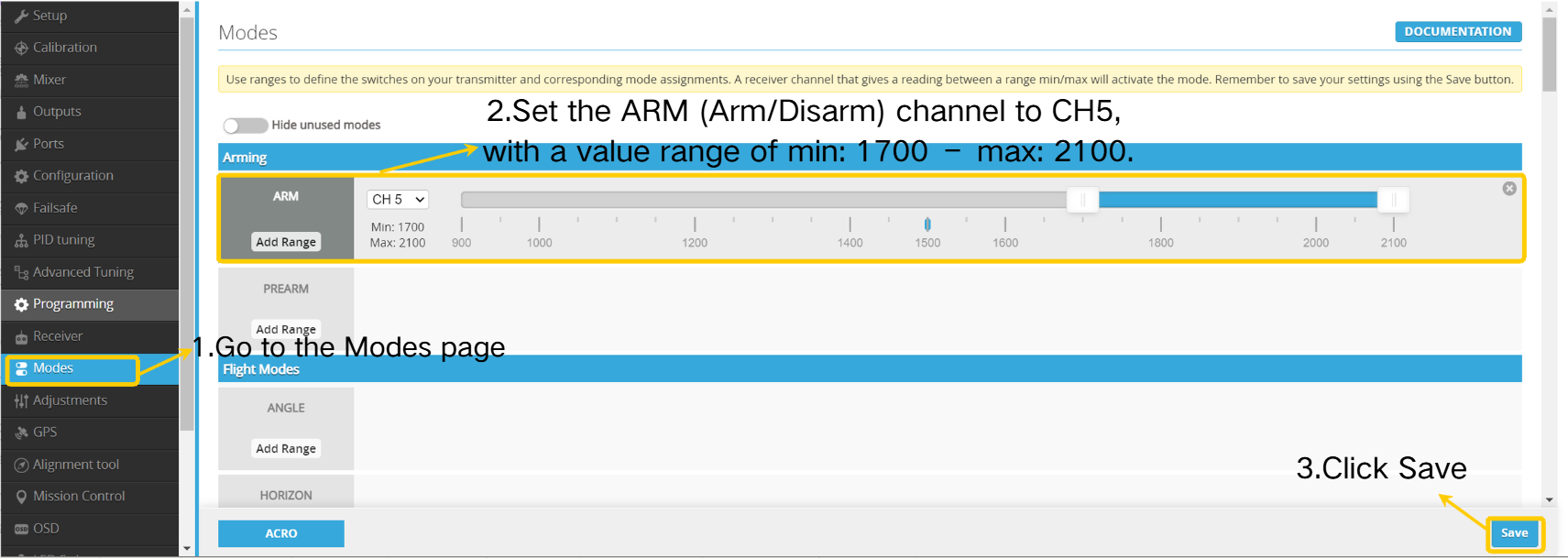
- Navigate to the Modes page.
- Set the ARM channel to CH5, with the range set between min:1700 and max:2100.
- Click " Save”.
3.5.3 Return-to-Home (RTH) Channel Setup
1. Radio Controller Settings
- Select a two-position switch.
- Navigate to the MDL/MIXES page and assign this switch to CH6 (this channel can be set according to your preference; provided here for reference only).
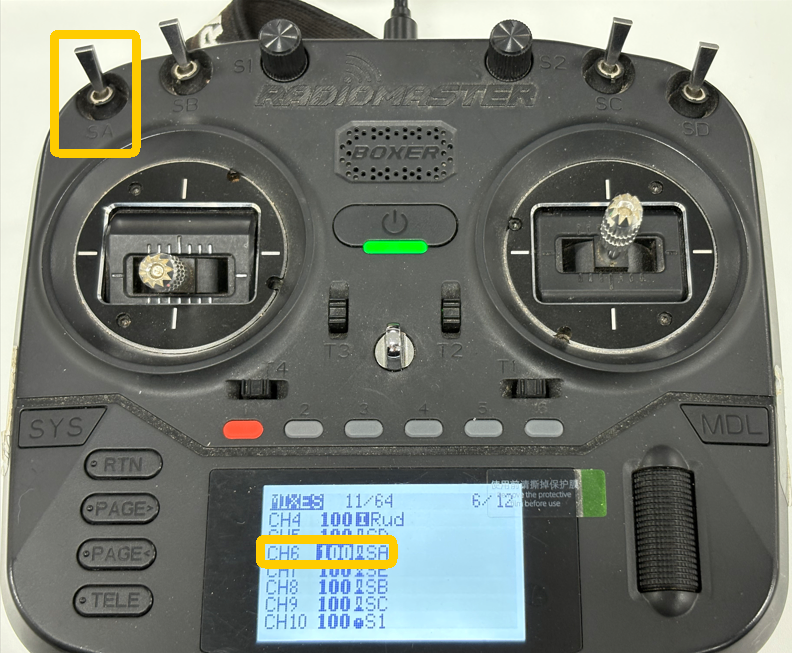

2. Activating the RTH Switch
By default, Return-to-Home mode activates only when the airplane is beyond 5 meters from the launch point; RTH will not appear in the OSD within 5 meters.
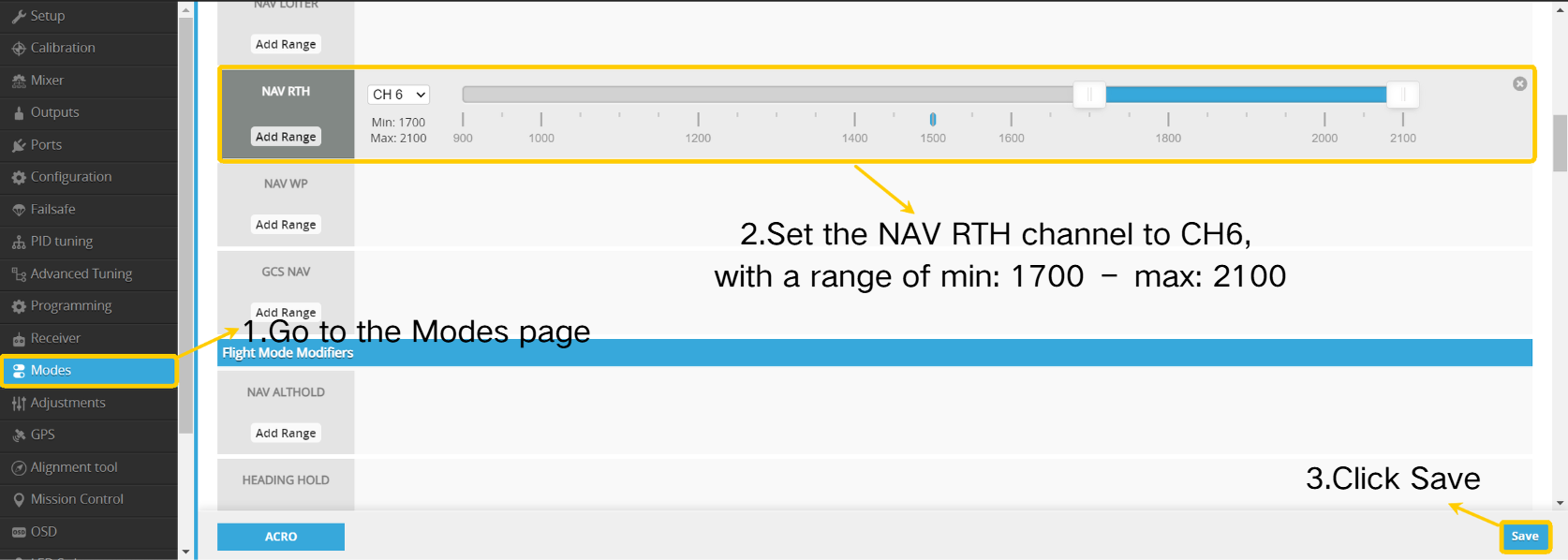
- Navigate to the Modes page.
- Set the NAV RTH channel to CH6, with the range set between min:1700 and max:2100.
- Click " Save”.
3.5.4 Flight Mode Configuration
1. Radio Controller Settings
- Select a three-position switch to configure three distinct flight modes.
- Navigate to the MDL/MIXES page and assign this switch to CH8.

2. Ground Station Setup
- Navigate to the Modes page.
- Set ANGLE mode to CH8 according to the illustration below; to extend the value range, click " Add range”.
- Combine AUTOTUNE mode with ANGLE mode as illustrated below.
- Click " Save”.
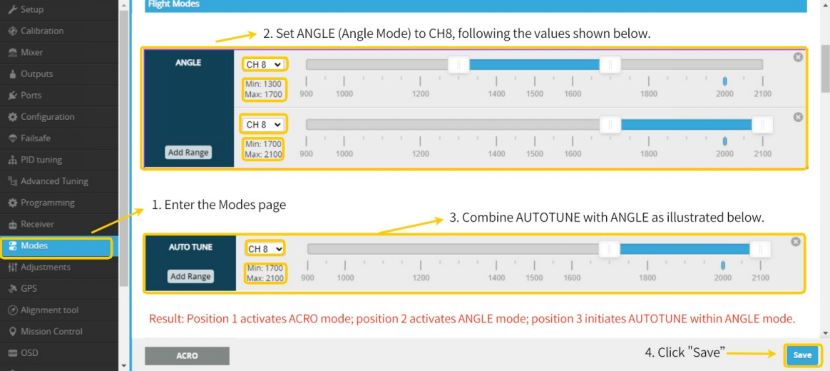
Result: The first position corresponds to ACRO mode, the second to ANGLE mode, and the third activates AUTOTUNE within ANGLE mode.
For detailed flight mode explanations: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/fc/flight-modes.html
IV. Equipment Installation
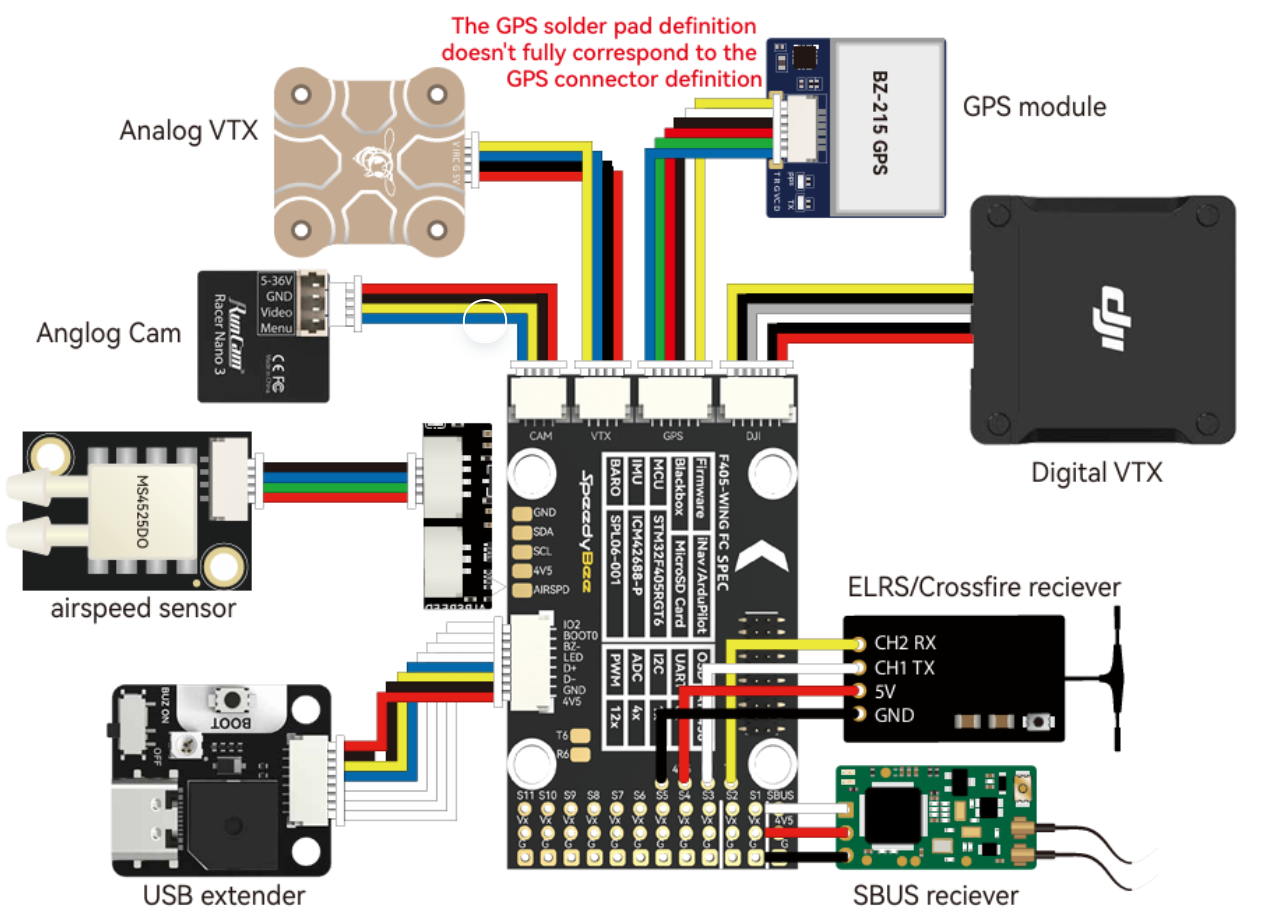
4.1 FC Wiring
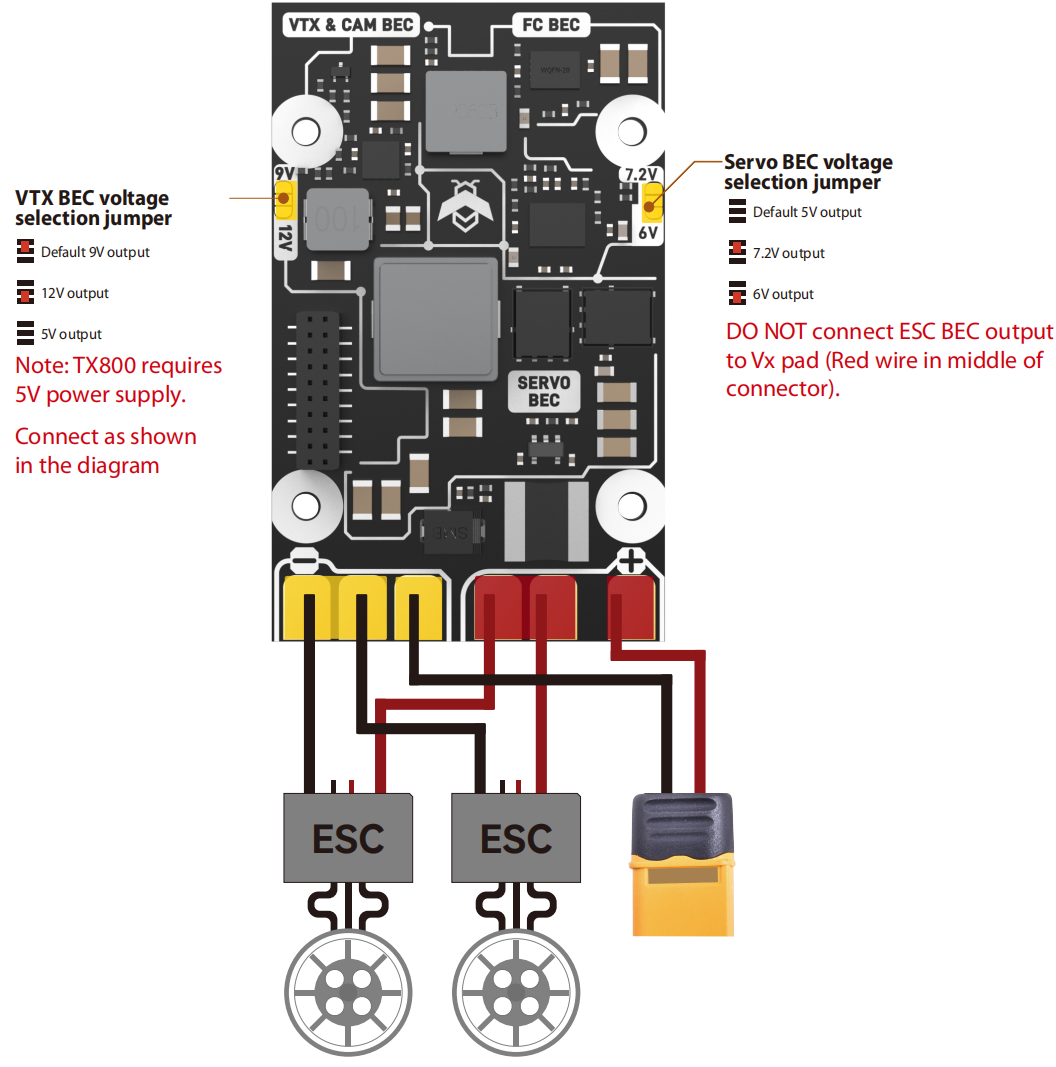
- Power Wiring
⚠️ Notes:
1.The positive wire must be connected to the specified pad
2.ESC refers to the electronic speed controller
3.Ensure solid solder joints to avoid cold soldering
4.2 FC Installation
Install the flight controller at the airplane's center of gravity, referring to the illustration below for guidance:
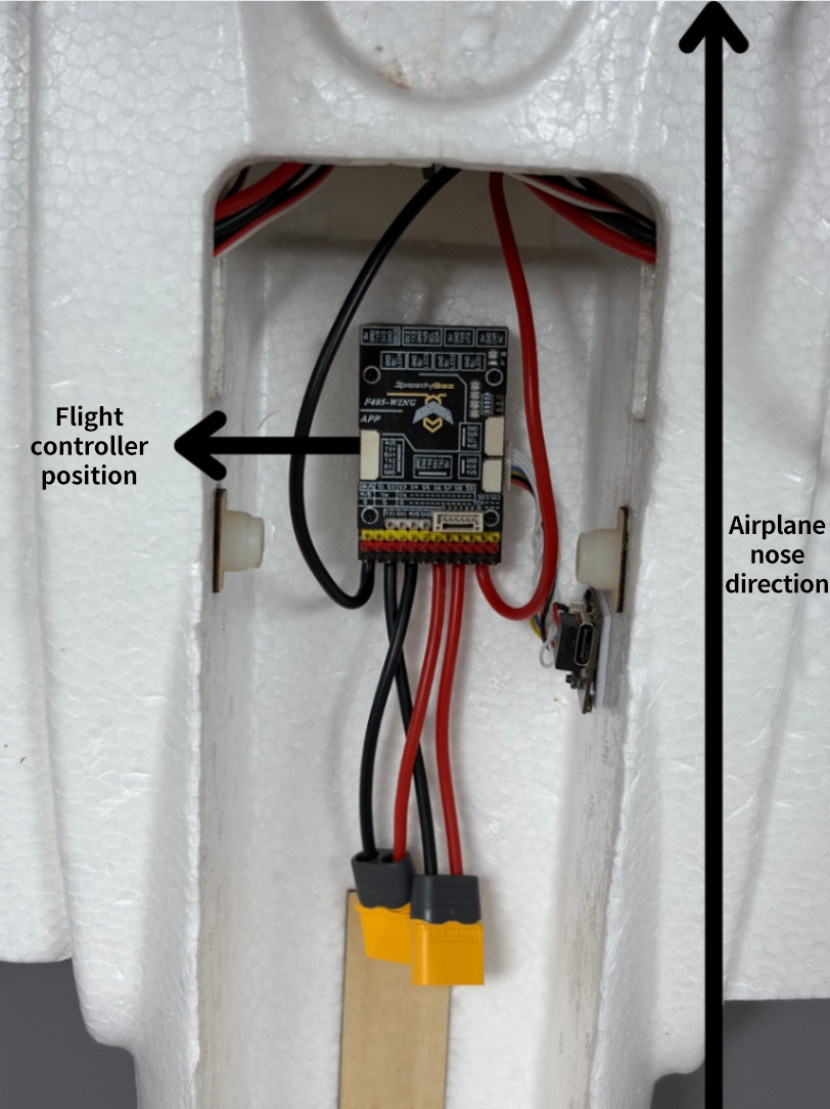
If you need to change the installation orientation: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/fc/fc-orientation.html
4.3 Peripheral Installation & Configuration
- Peripheral wiring
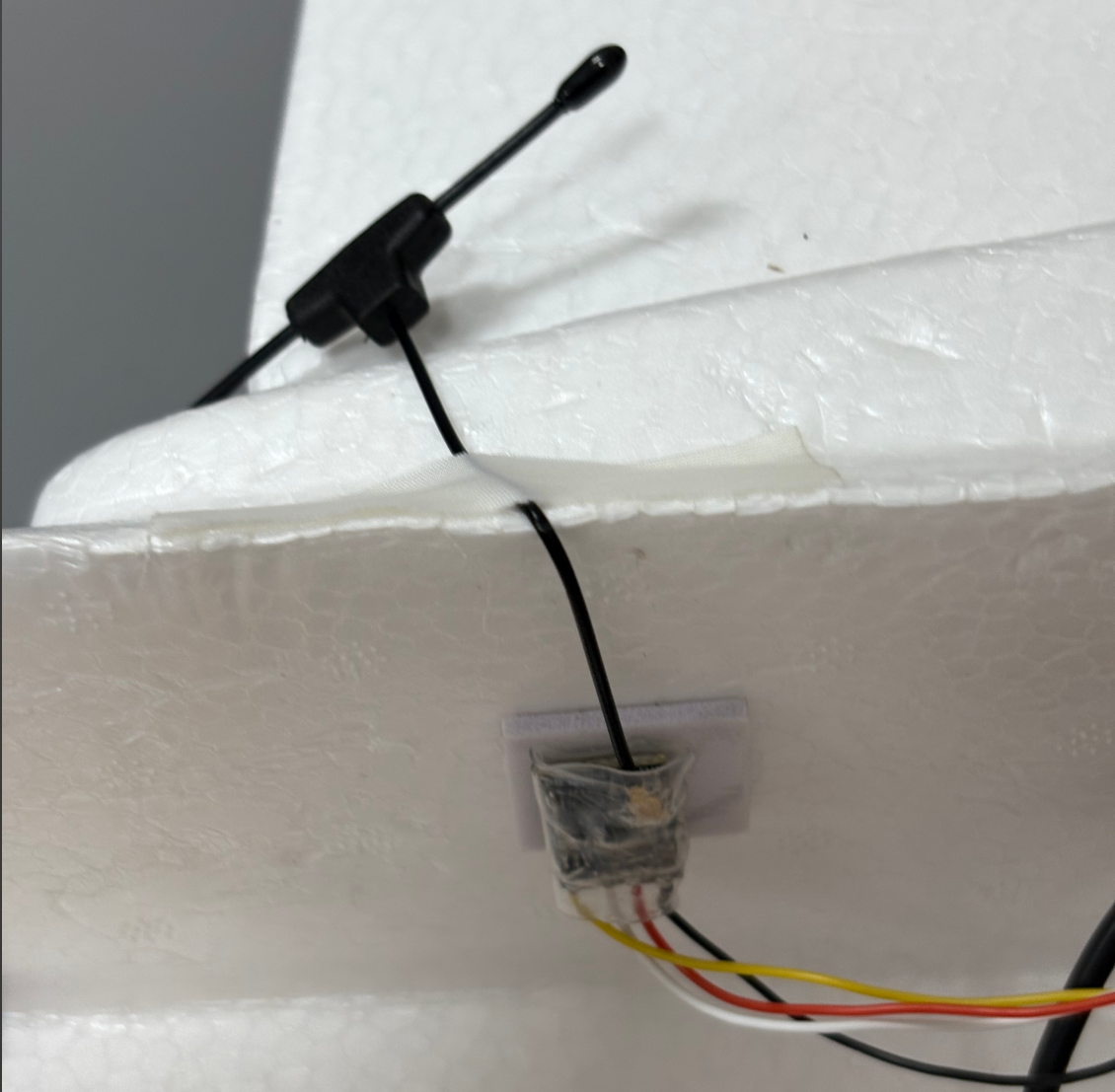
4.3.1 Receiver Installation
Refer to the diagram for mounting position.Route the antennas out of the fuselage and secure them with tape.
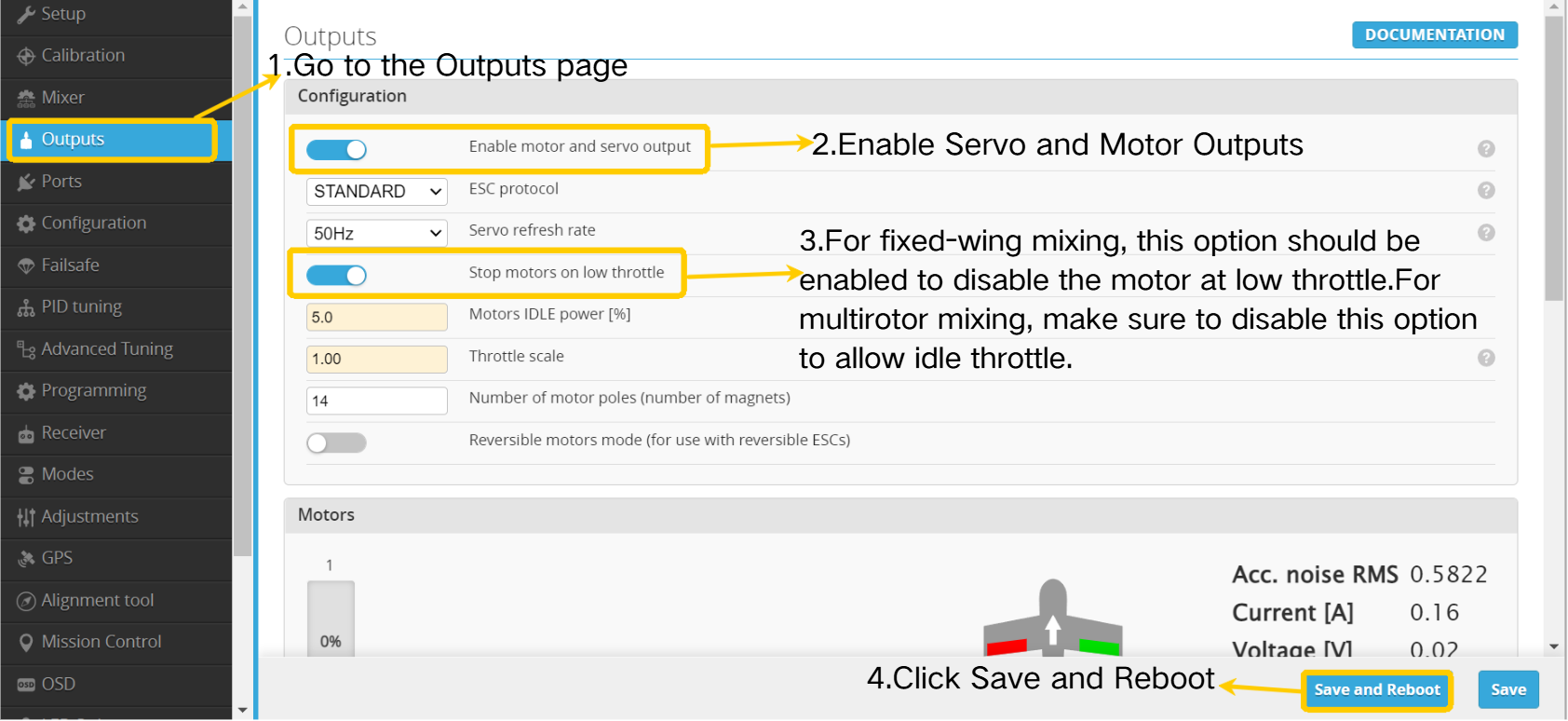
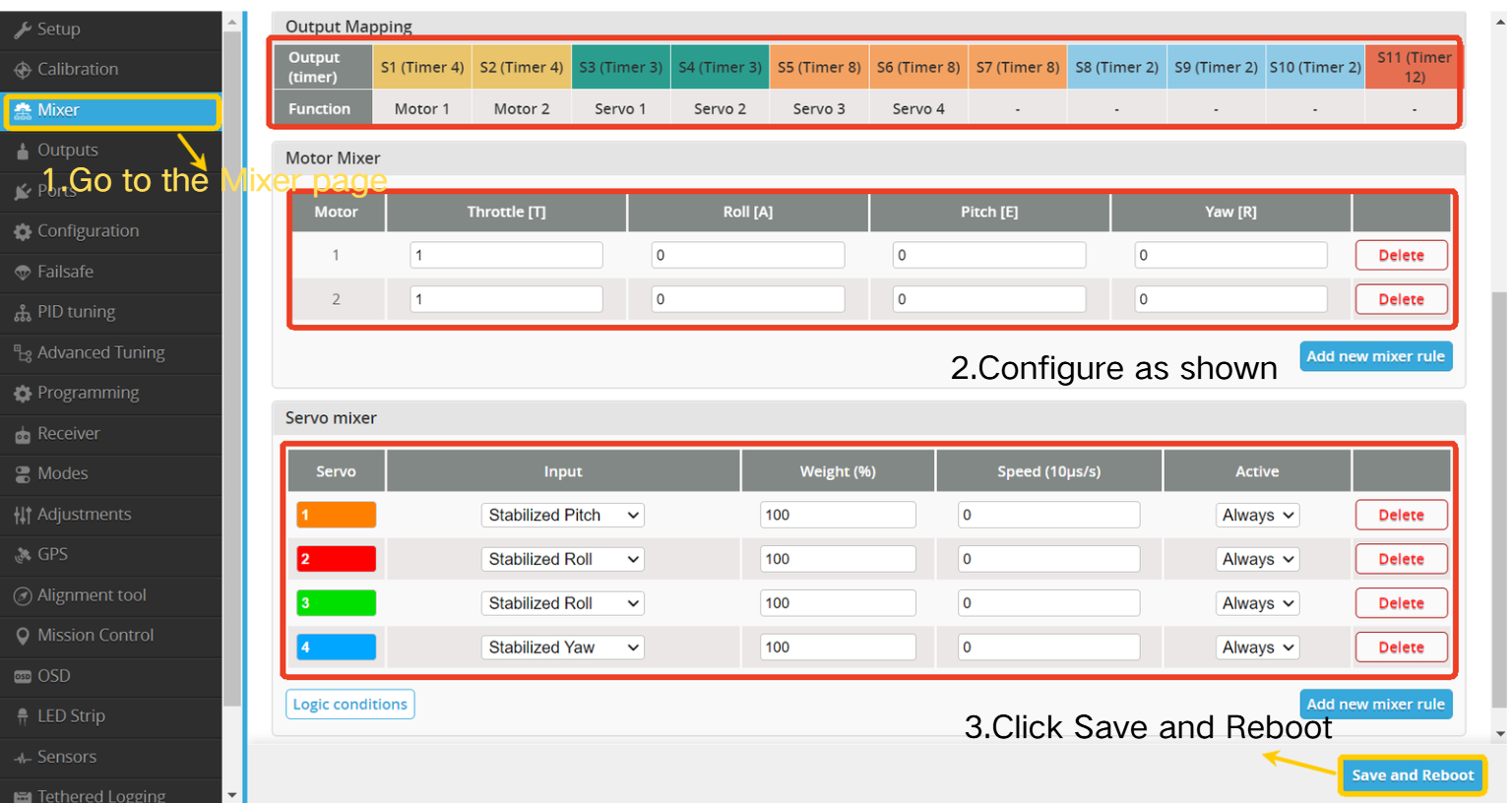
4.3.2 Mixer Setup (Servos and Motors) & Surface Check
Enable Servo and Motor Outputs:
1. Motors and servos will only function after servo and motor outputs are enabled.
2. In fixed-wing mode, ensure "Motor Stop on Low Throttle" is enabled to prevent unintended motor spin after arming, avoiding unnecessary damage.
3. For multirotor mixing, remember to disable "Motor Stop on Low Throttle" to allow idle spinning.
Output Wiring:
The flight controller includes a built-in BEC. If your ESC also has a built-in BEC, remove and insulate the middle power wire carefully to prevent short circuits caused by movement during flight! ! !
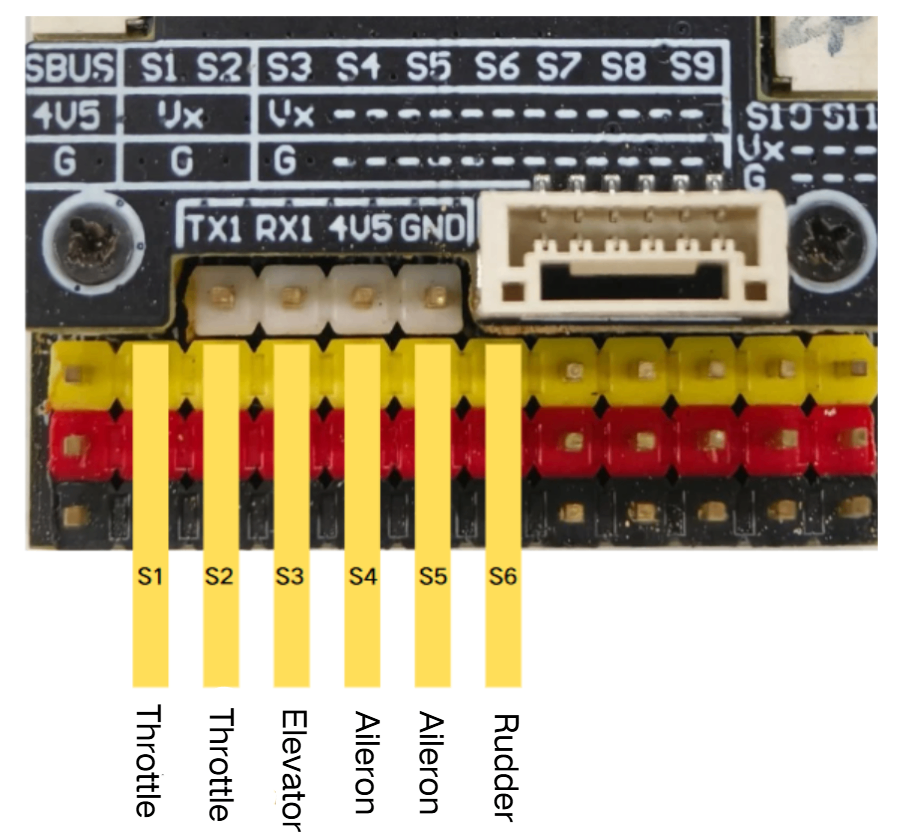
Parameter Setup:
- Navigate to the Mixer page.
- Configure settings according to the illustrations.
- Click "Save and Reboot”.
| Channel | Function |
|---|---|
| S1 | Throttle |
| S2 | Throttle |
| S3 | Elevator |
| S4 | Aileron |
| S5 | Aileron |
| S6 | Rudder |
Control Surface Check:
a. Stabilized mode control surface feedback check
First, calibrate the compass,Wait 30 seconds , Click Save and Reboot
Switch flight mode to ANGLE
- When the airplane rolls left, the left wing control surface moves downward, and the right wing control surface moves upward.
- When the airplane rolls right, the left wing control surface moves upward, and the right wing control surface moves downward.
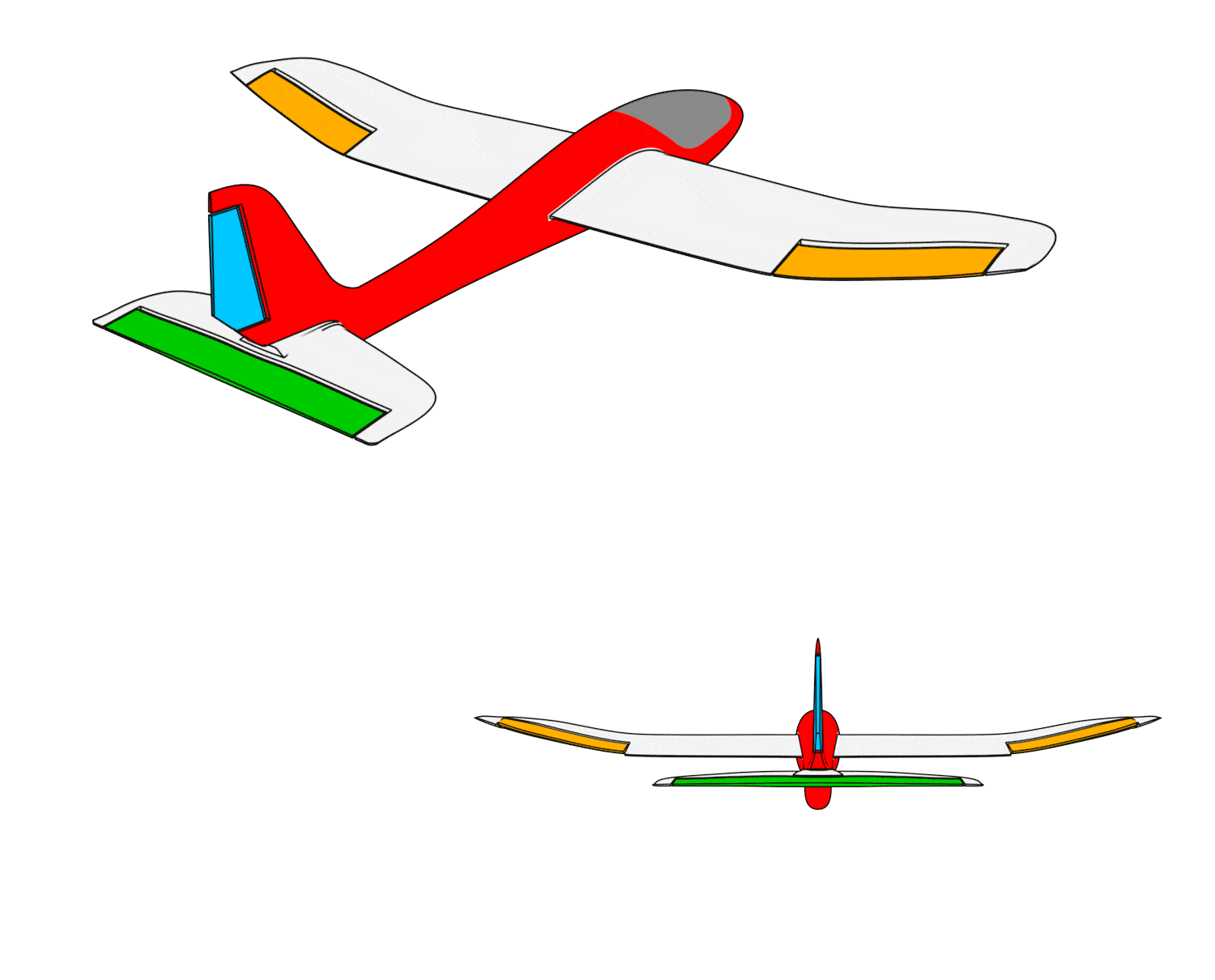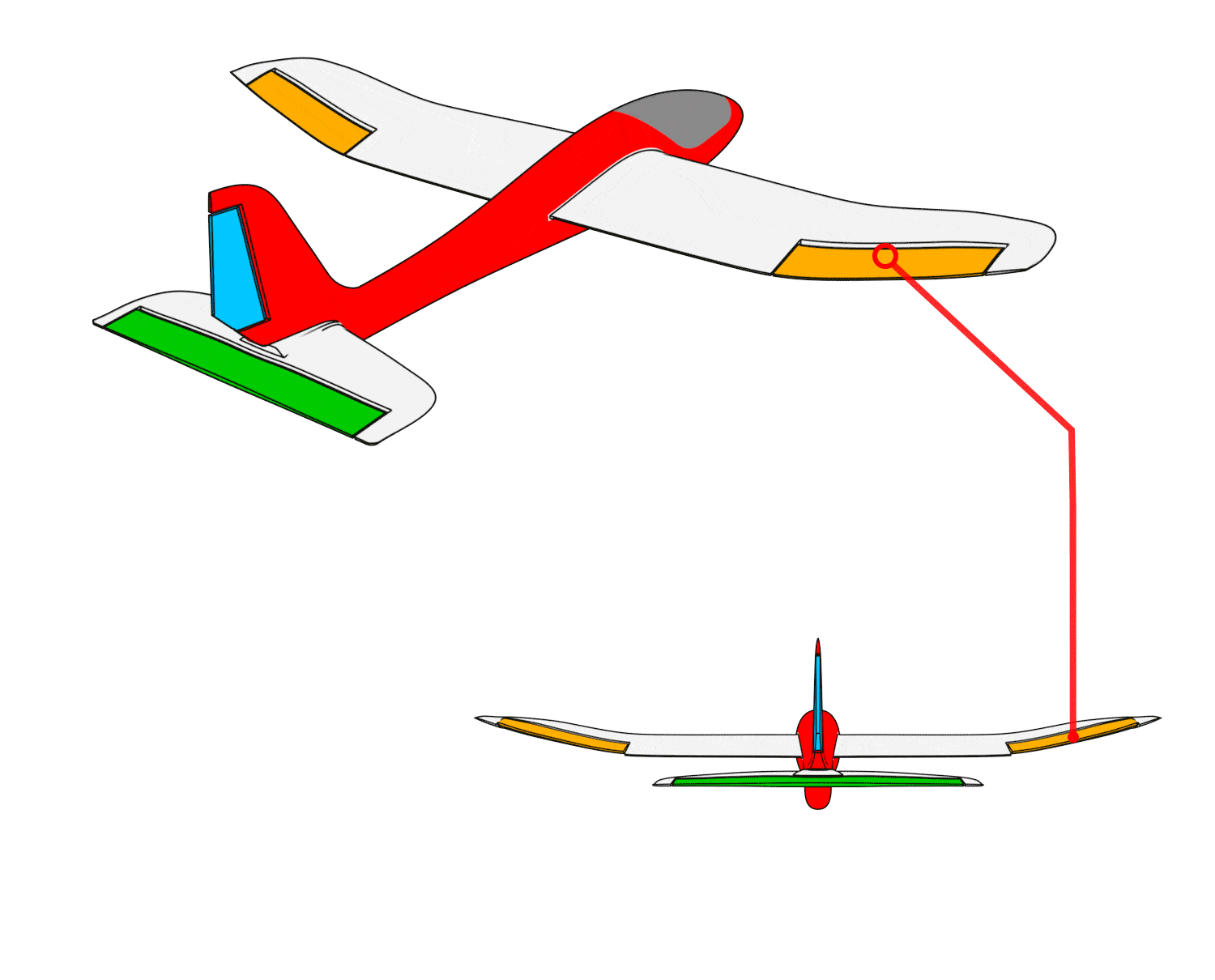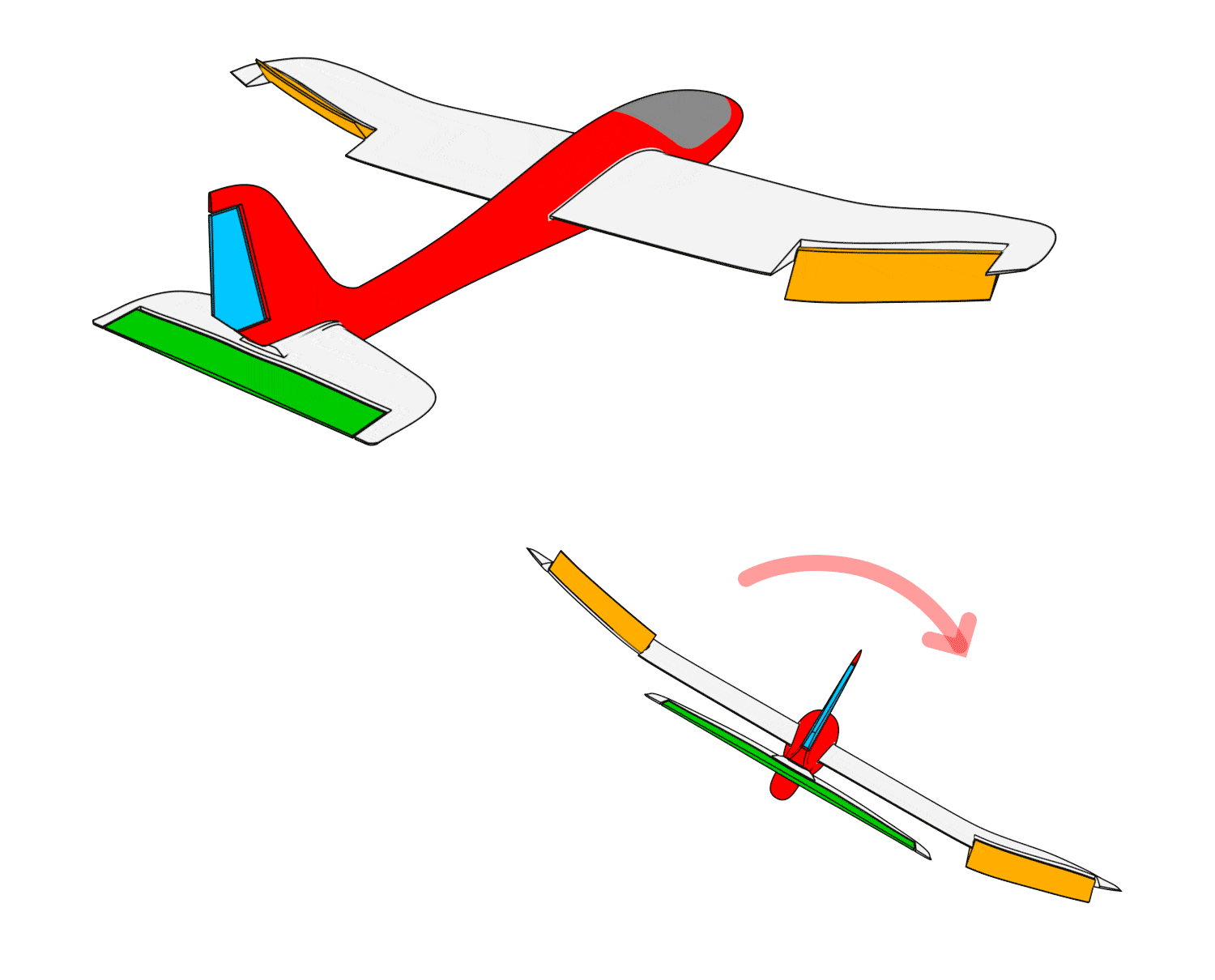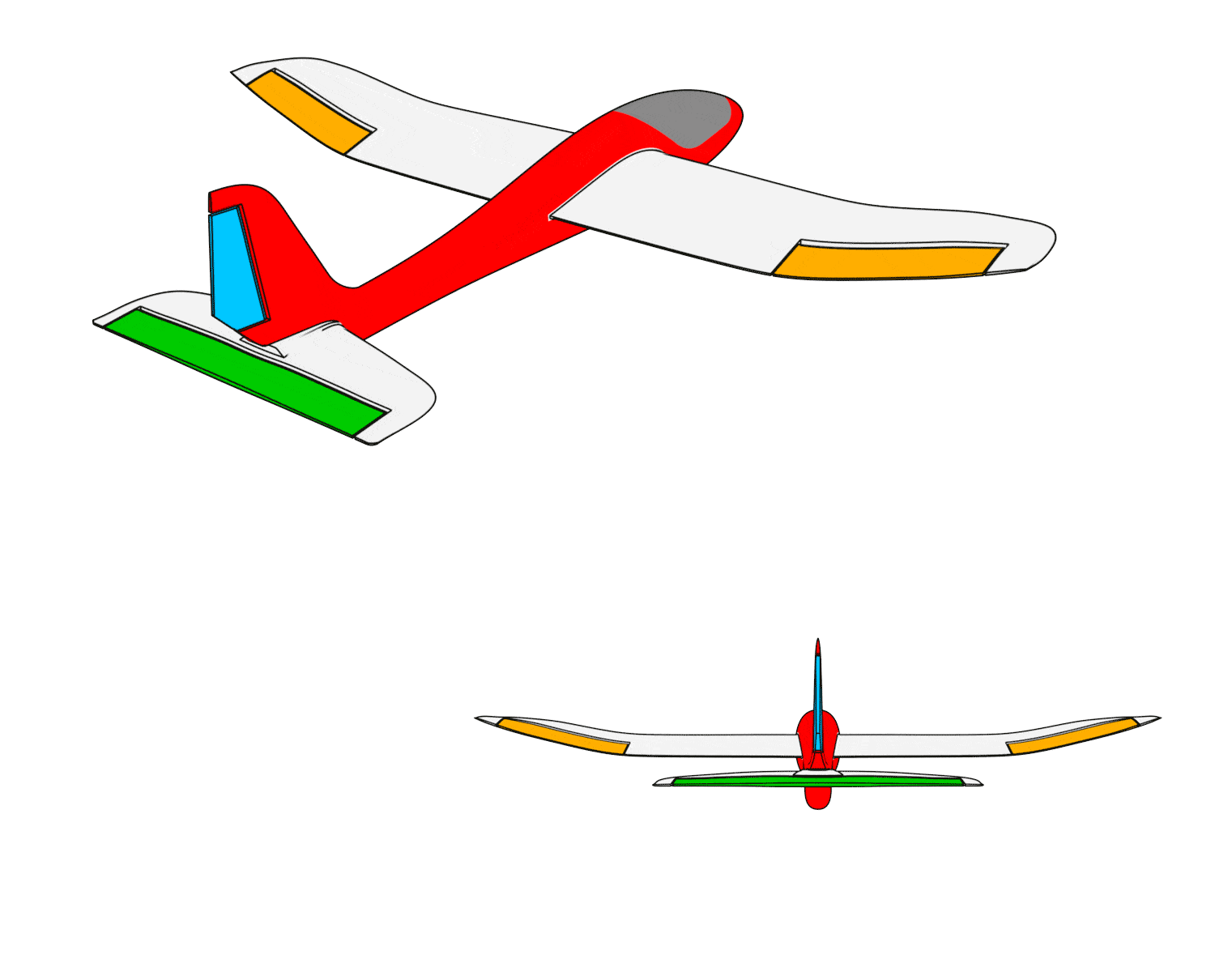
- When the airplane pitches upward, the elevator moves downward.
- When the airplane pitches downward, the elevator moves upward.
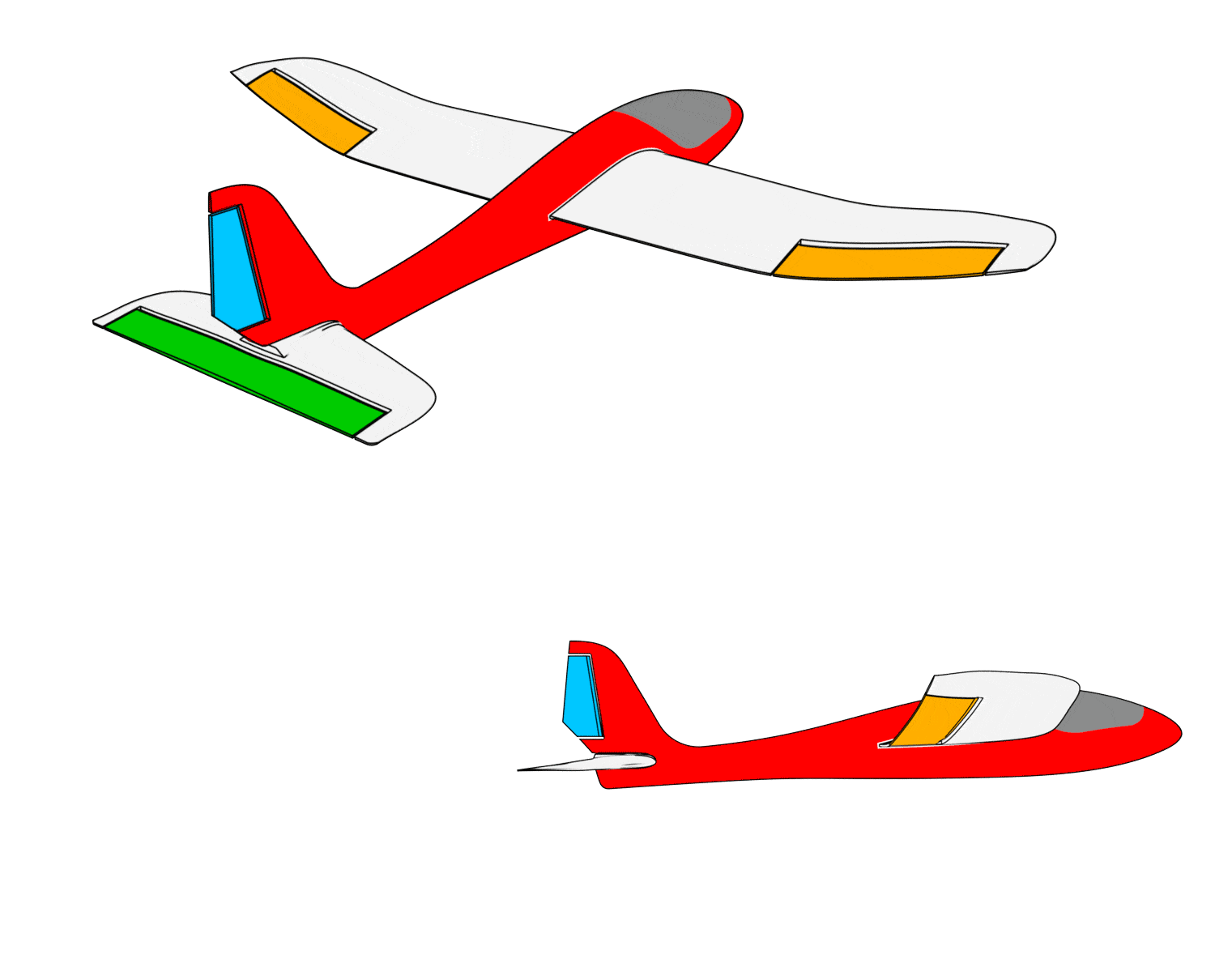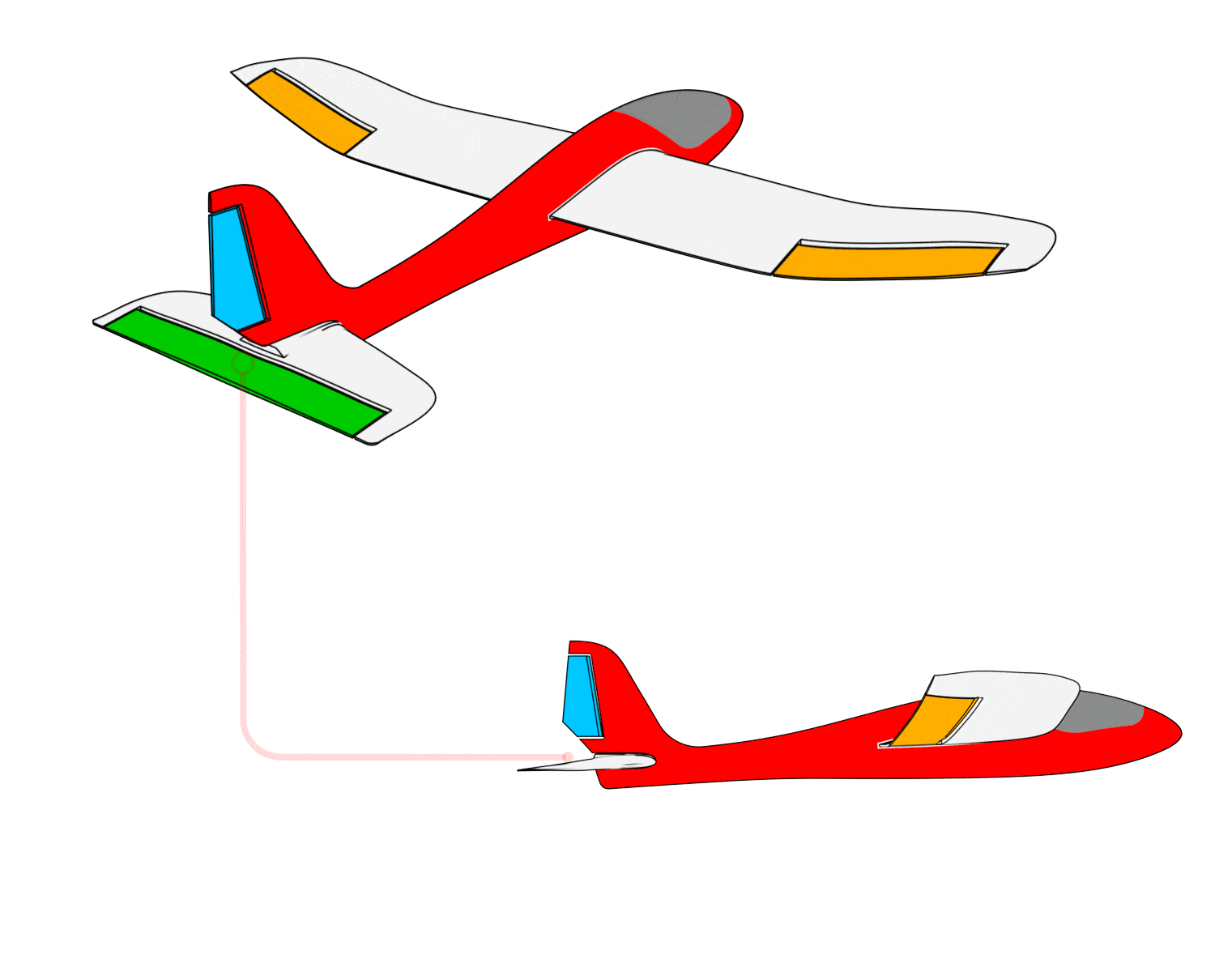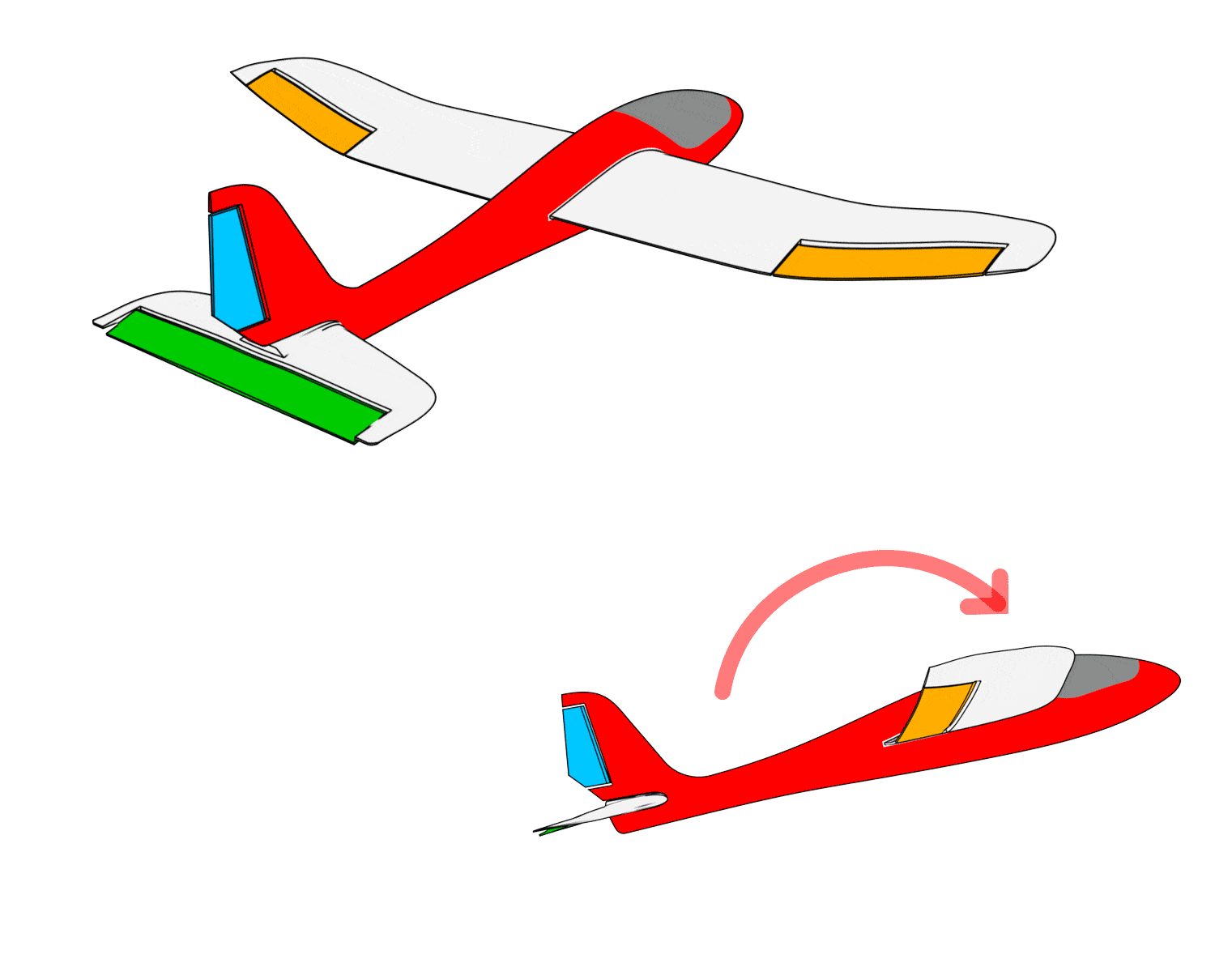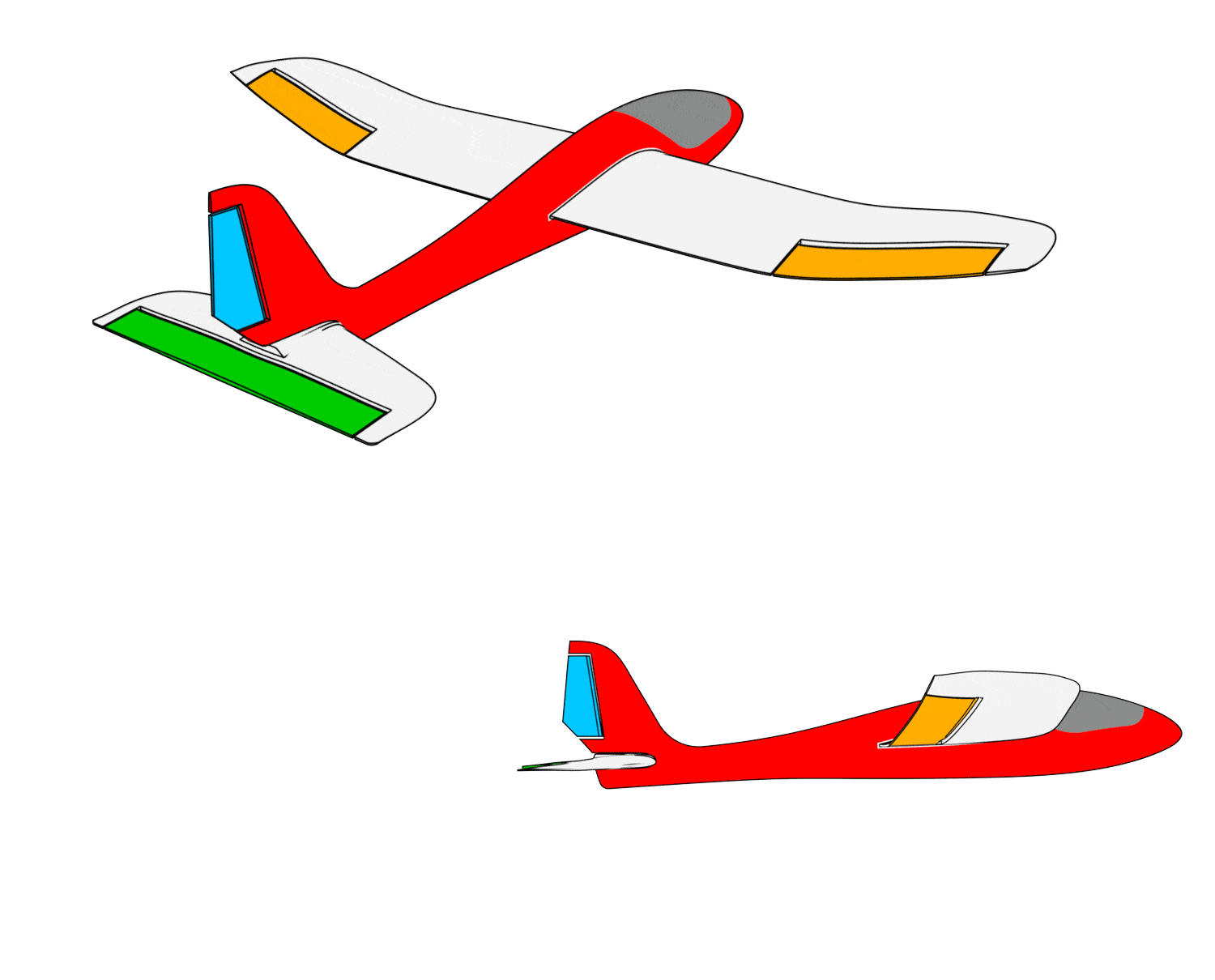
b. Manual mode control surface feedback check
Switch the flight mode to ACRO
- When the aileron stick is pushed left, the left wing control surface moves upward, and the right wing control surface moves downward.
- When the aileron stick is pushed right, the left wing control surface moves downward, and the right wing control surface moves upward.
- When pulling back on the elevator stick, the elevator control surface moves downward.
- When pushing forward on the elevator stick, the elevator control surface moves upward.
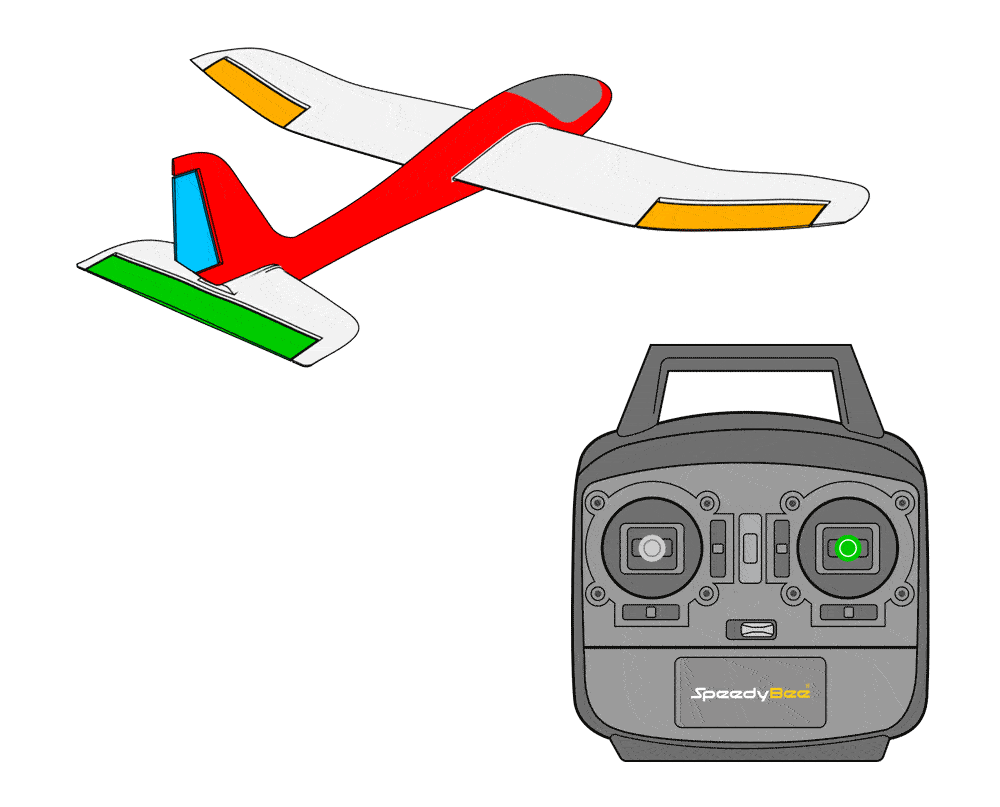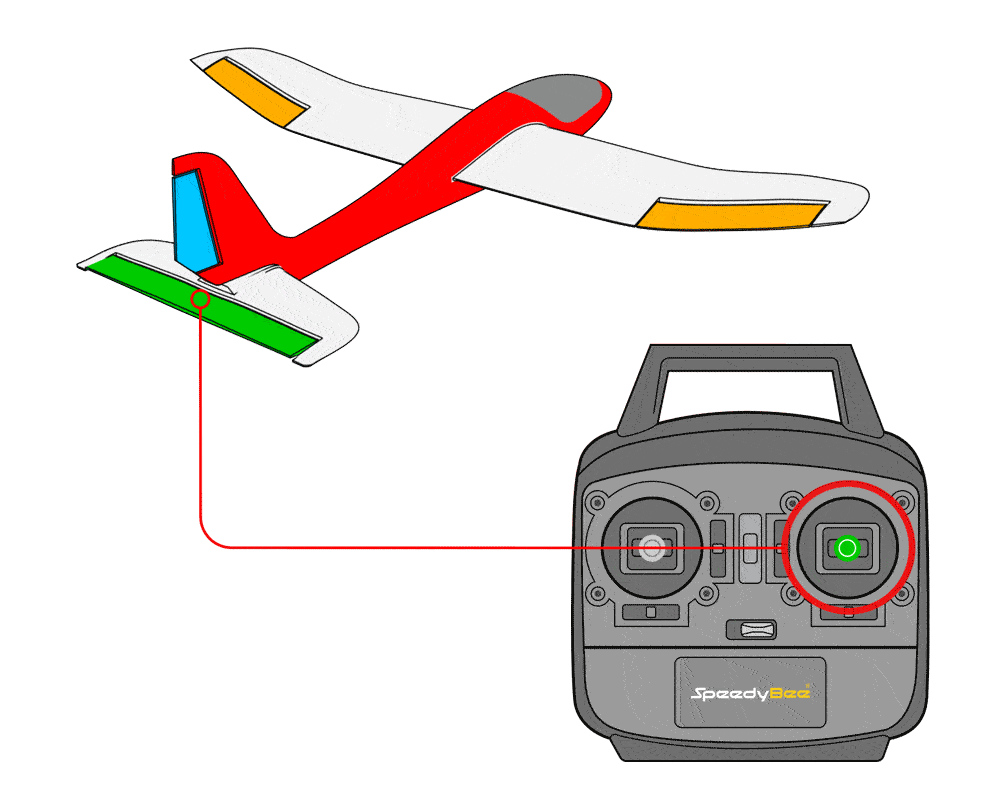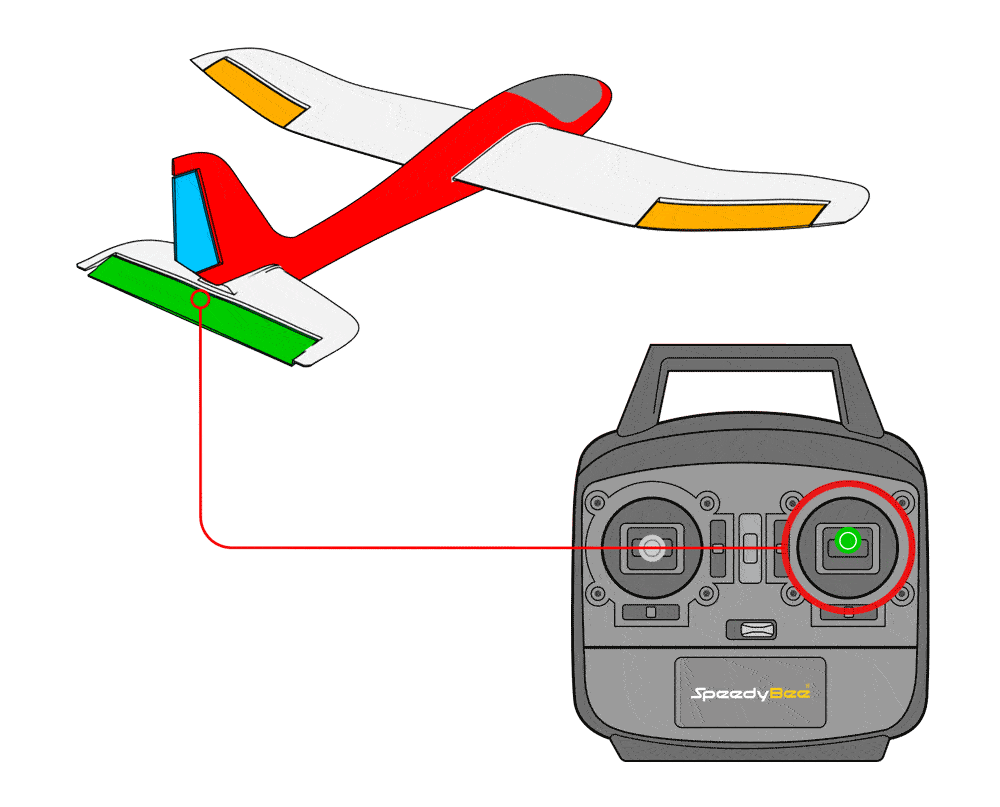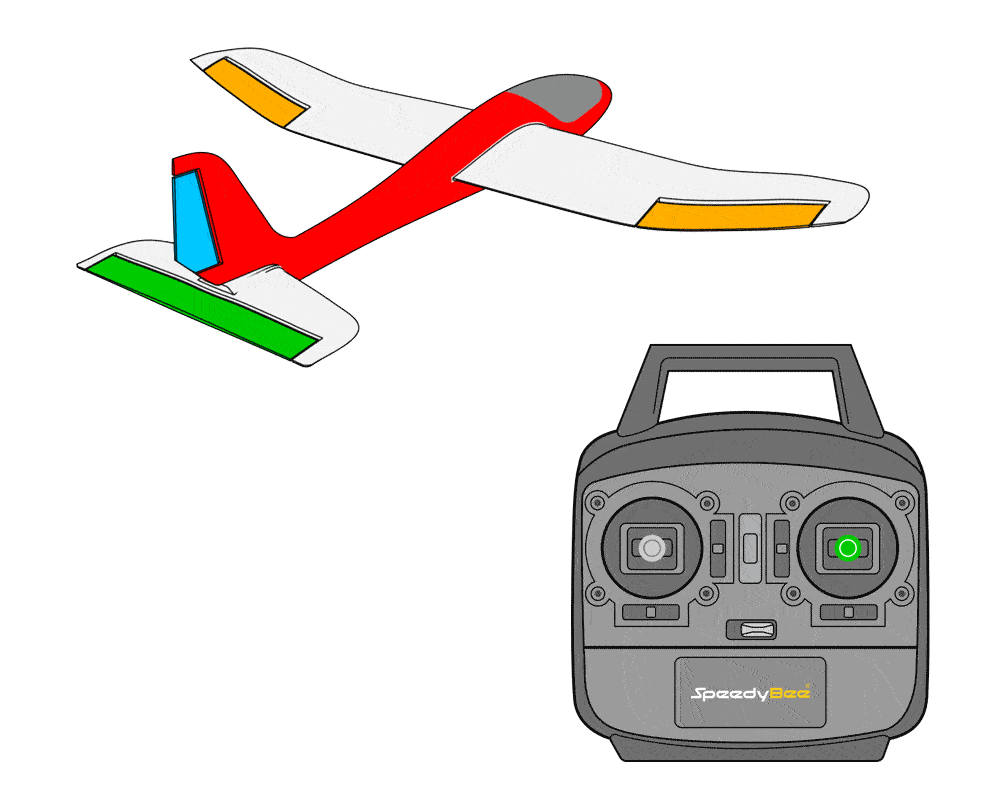
- When moving the rudder stick left, the rudder control surface moves to the left.
- When moving the rudder stick right, the rudder control surface moves to the right.
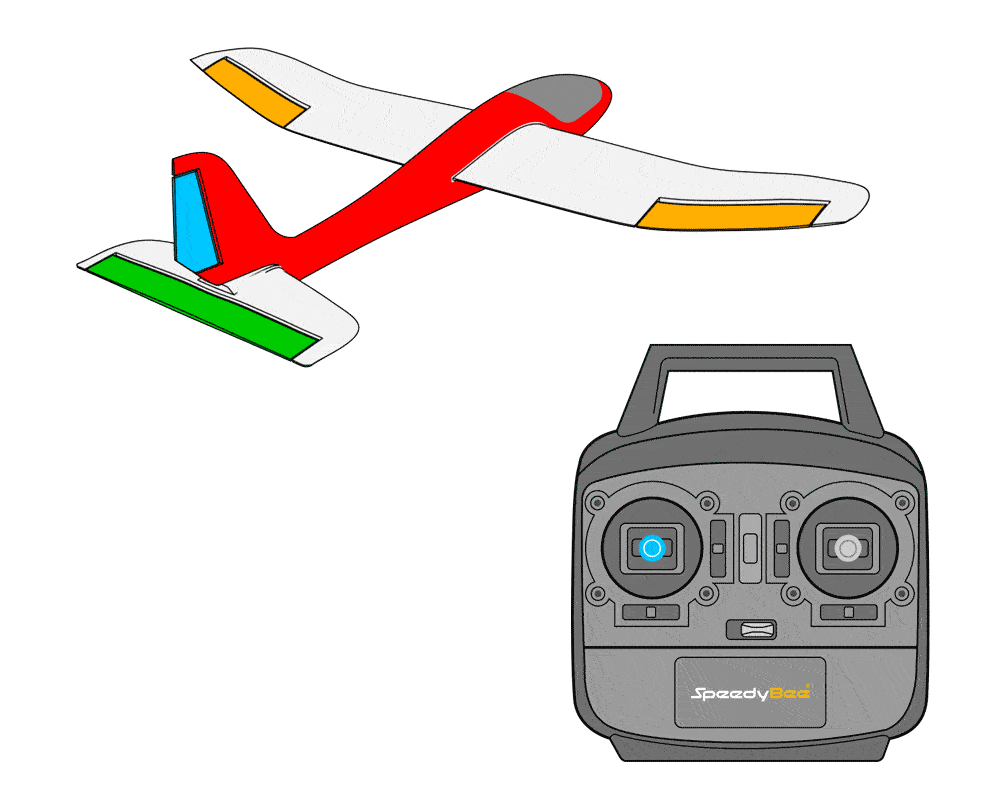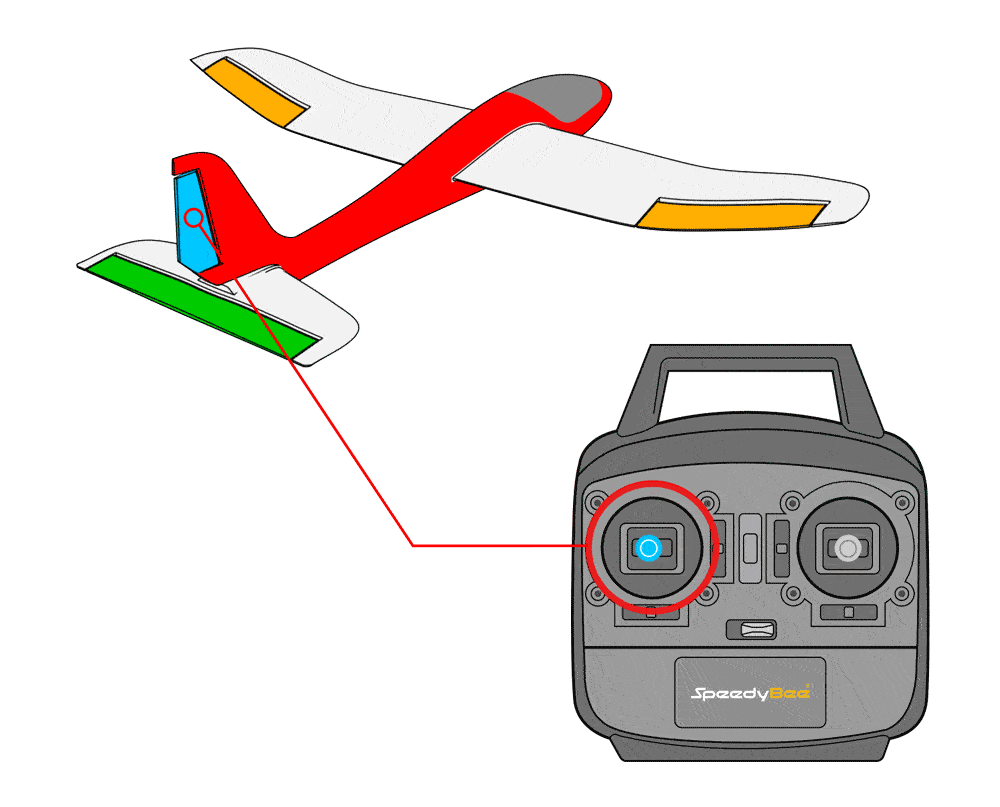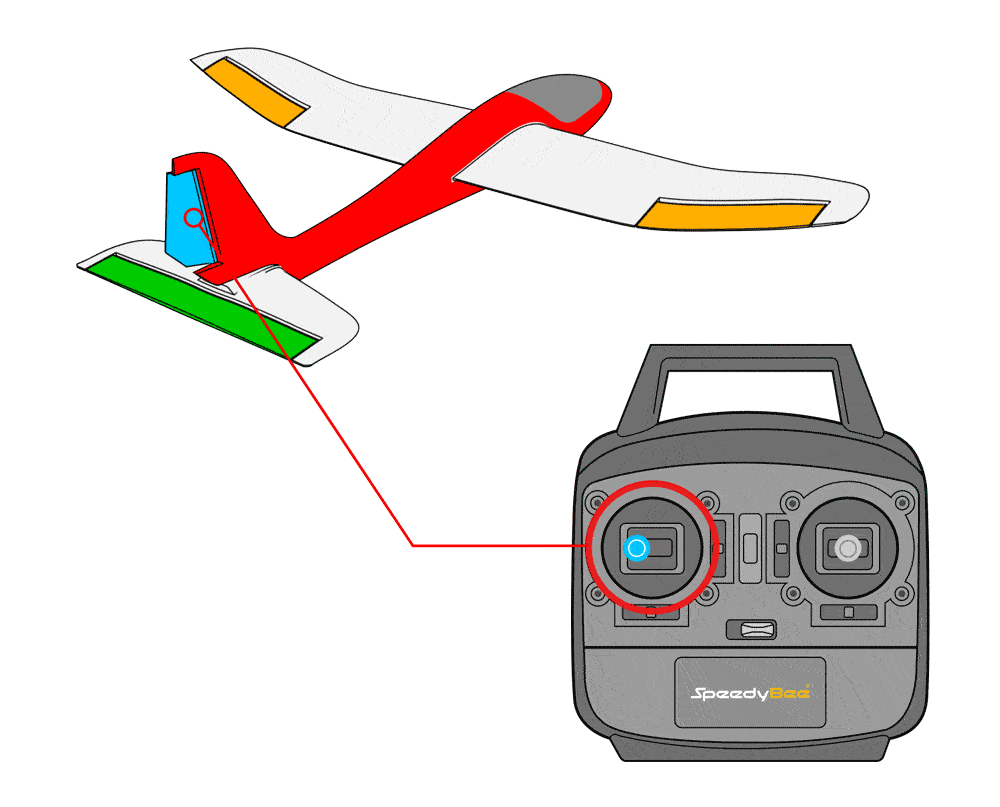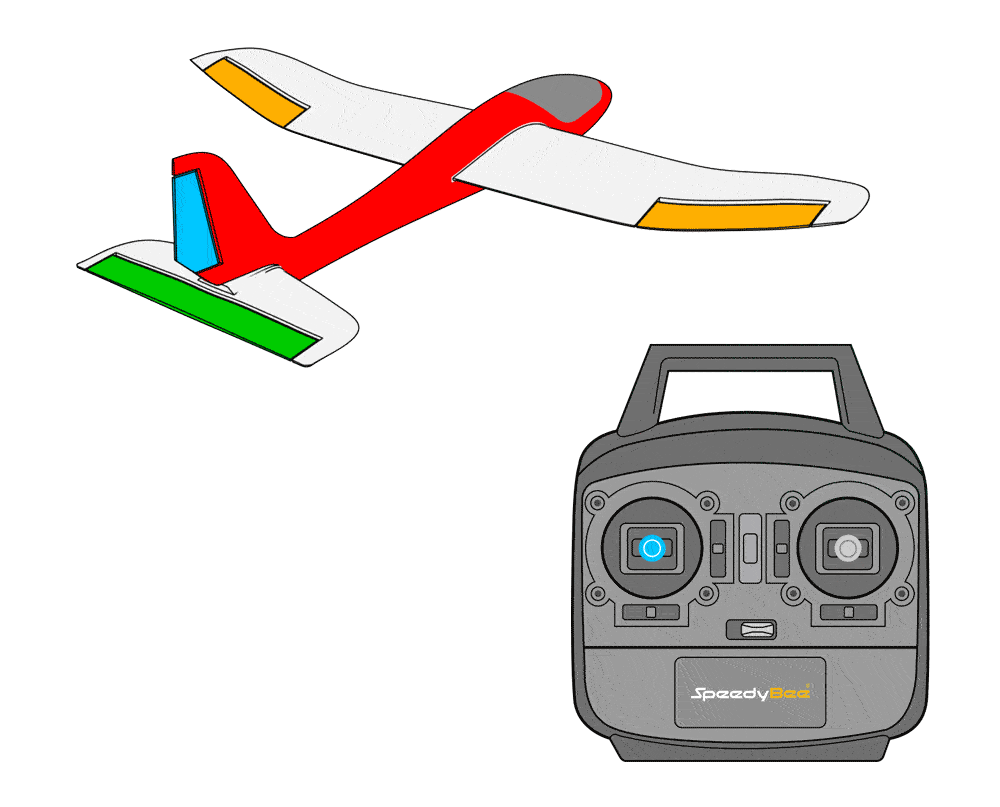
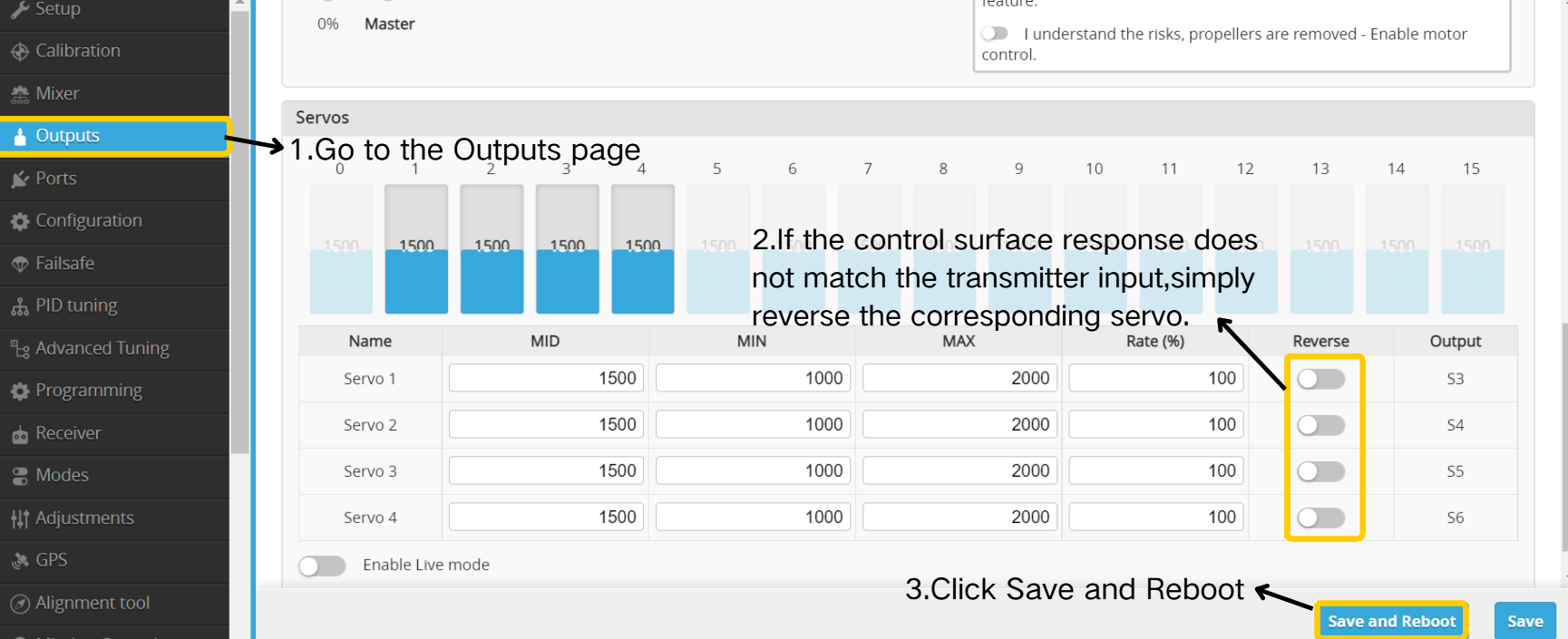
First, verify the feedback in stabilized mode; if incorrect, invert the value to reverse it.
For example, if you tilt the aircraft to the left while in stabilized mode, the control surfaces should attempt to level the aircraft.In this case, the left aileron should move down and the right aileron should move up.If the left aileron moves in the opposite direction, you can fix it by reversing SERVO1.
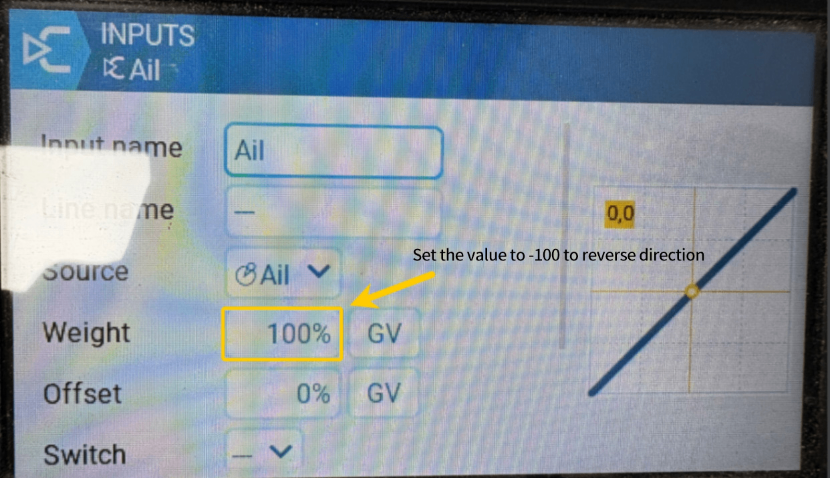
Then verify manual mode feedback; if incorrect, reverse the corresponding channel on the radio controller.
Using an EdgeTX radio system as an example, navigate to MDL → INPUT and set the "Weight" value to -100 to invert manual feedback.

4.3.3 GPS Installation and Setup
- Install the GPS module as illustrated. Secure it firmly using 3M adhesive tape on the bottom to prevent instability during flight.
Ensure the module is installed level and vertical; incorrect alignment prevents accurate orientation settings.
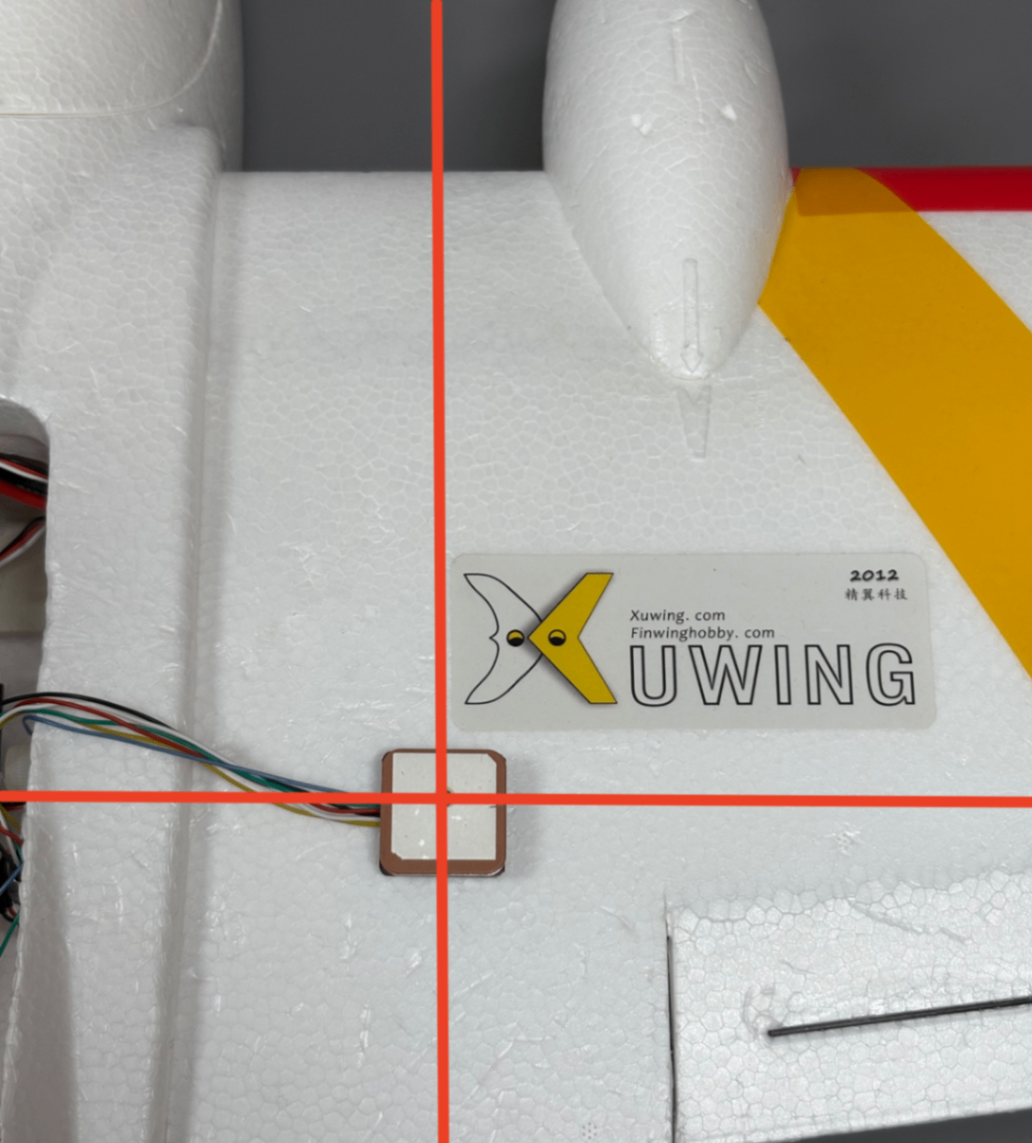
1. Avoid installing near metallic components, such as magnetic hatch covers or metal rods, to prevent compass interference.
2. Keep away from receivers, servo wires, motors, and similar components to avoid compass interference.
3. Confirm the module is securely mounted.
4. For detailed installation instructions for different modules, refer to their manuals.
For detailed instructions on how to install and configure the compass orientation, please refer to the following article: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/gps/inav-compass-setup.html
Parameter Setup:
4.3.4 VTX Equipment Installation and OSD Configuration
Analog VTX Installation:
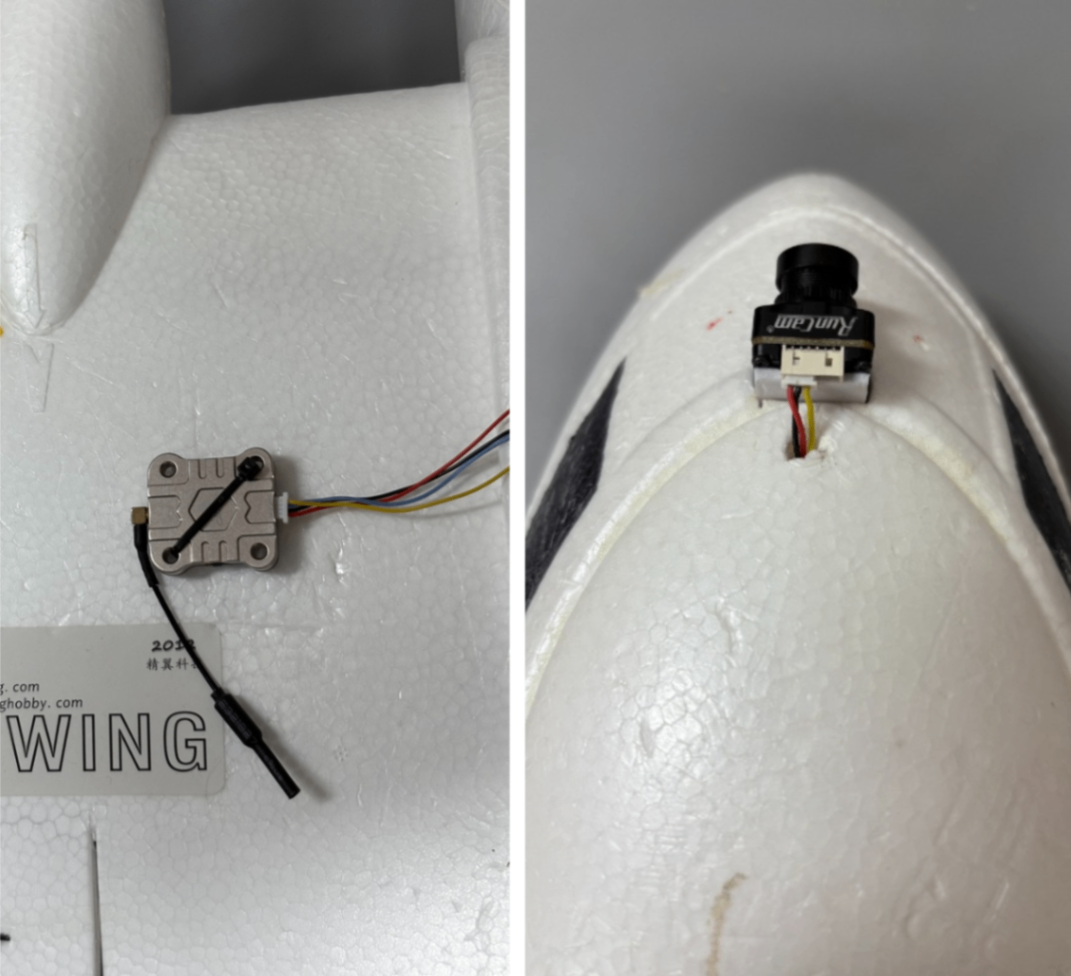
- Analog VTX Parameter Setup:
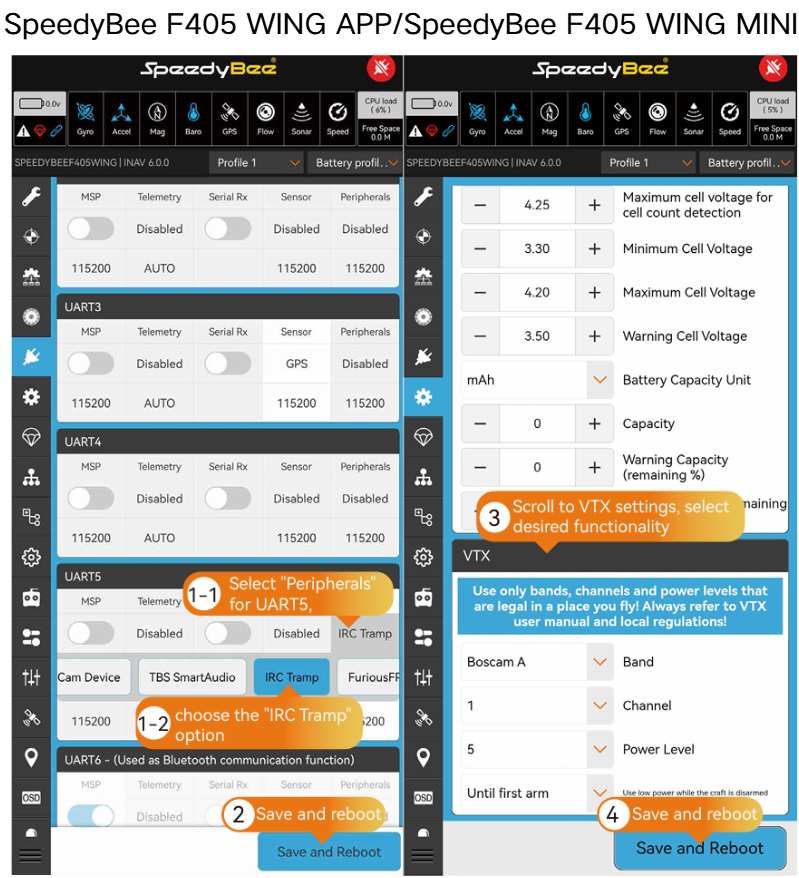
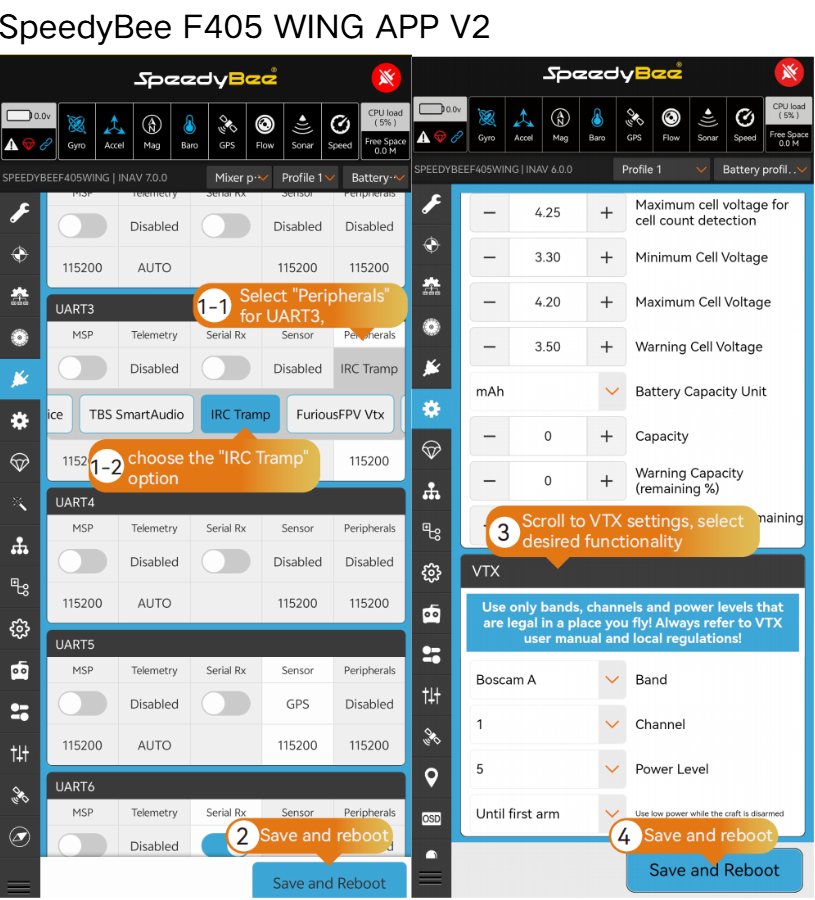
- HD VTX Installation:
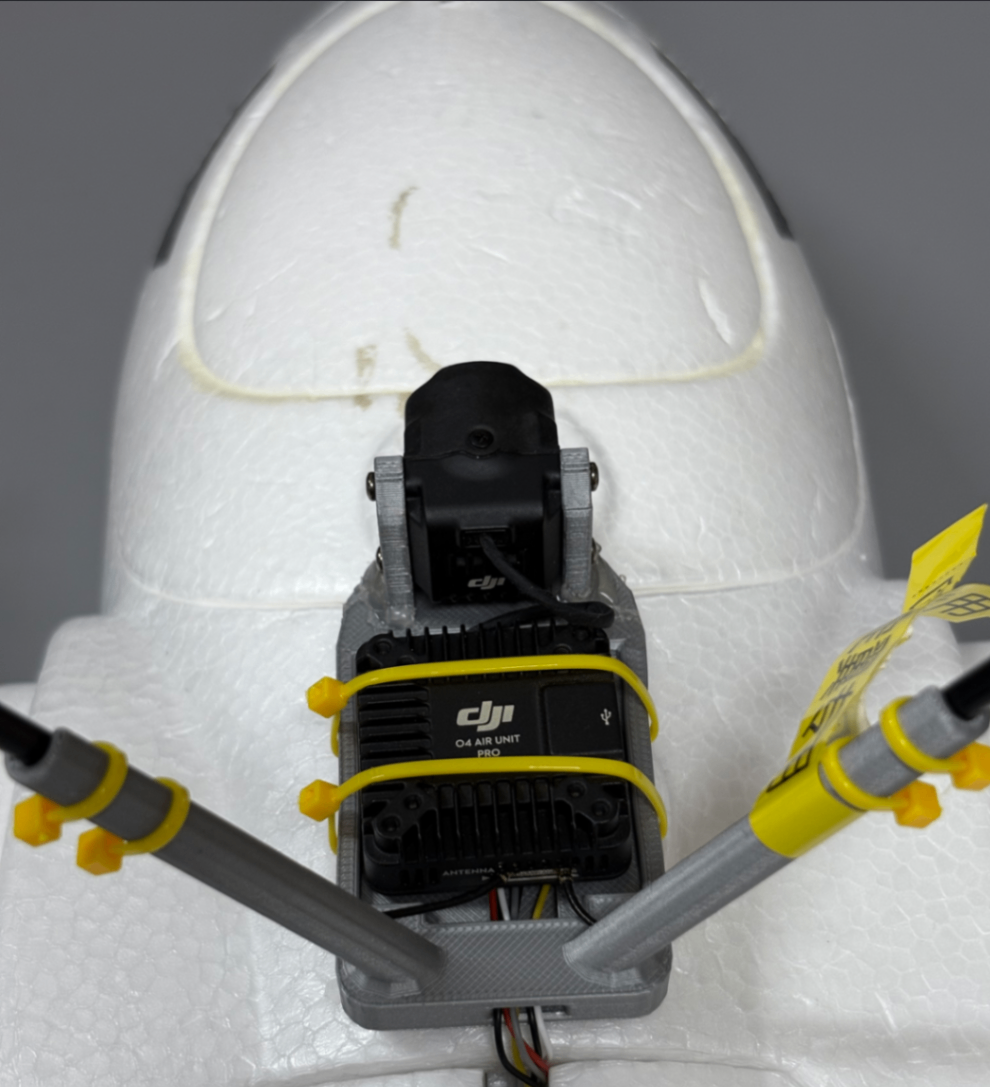

- HD VTX Parameter Setup:
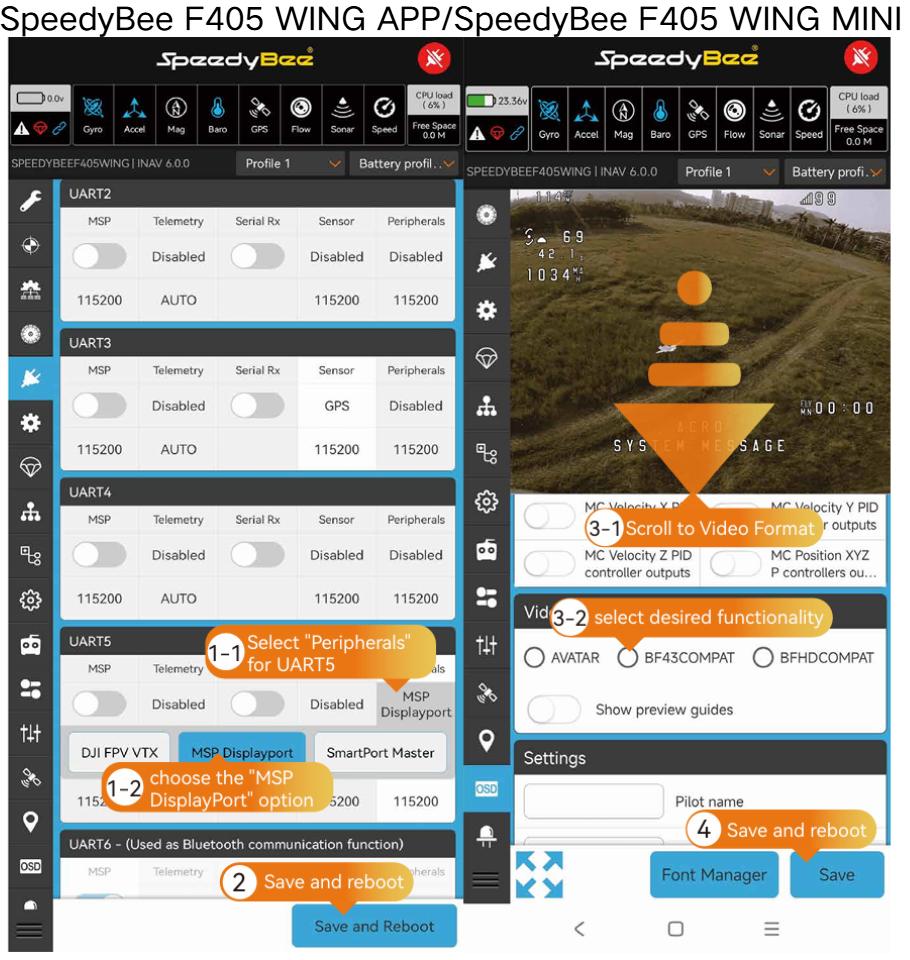
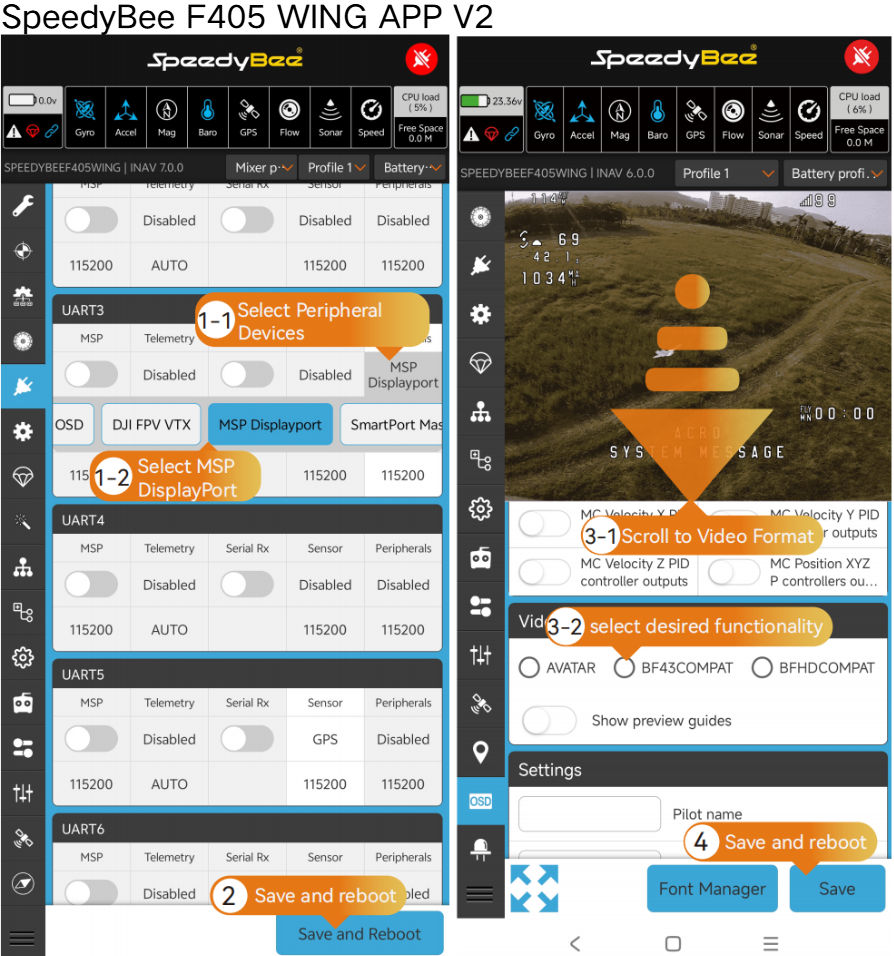
OSD Configuration:
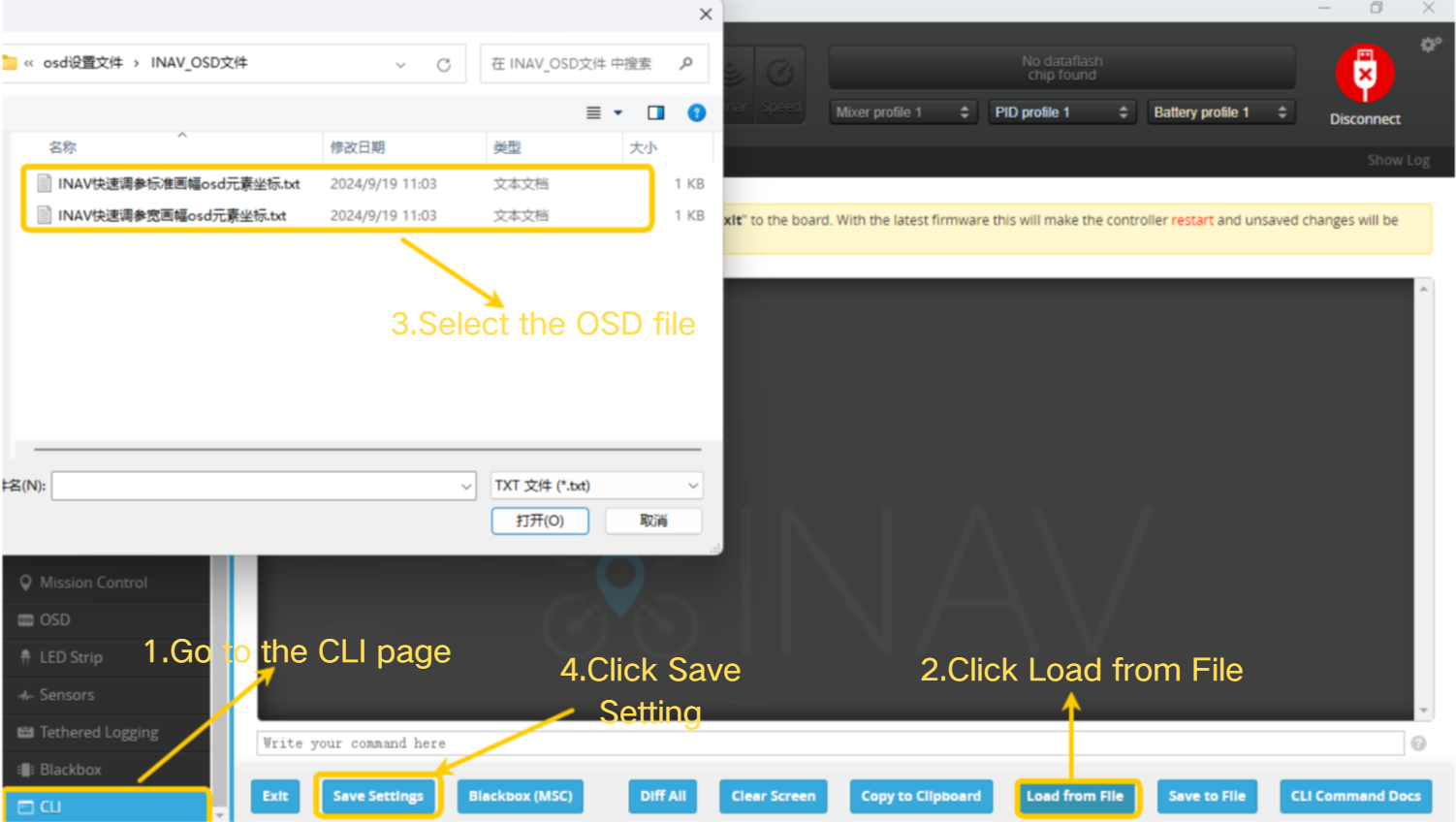
- OSD configuration file:INAV_OSD文件.zip can be downloaded and imported directly
- Enter the CLI page.
- Click " Load from File”.
- Select the OSD configuration file.
- Wait until the import is complete.
- Click " Save Setting”.
4.3.5 Airspeed Sensor Installation and Setup
Airspeed sensor mounting reference:
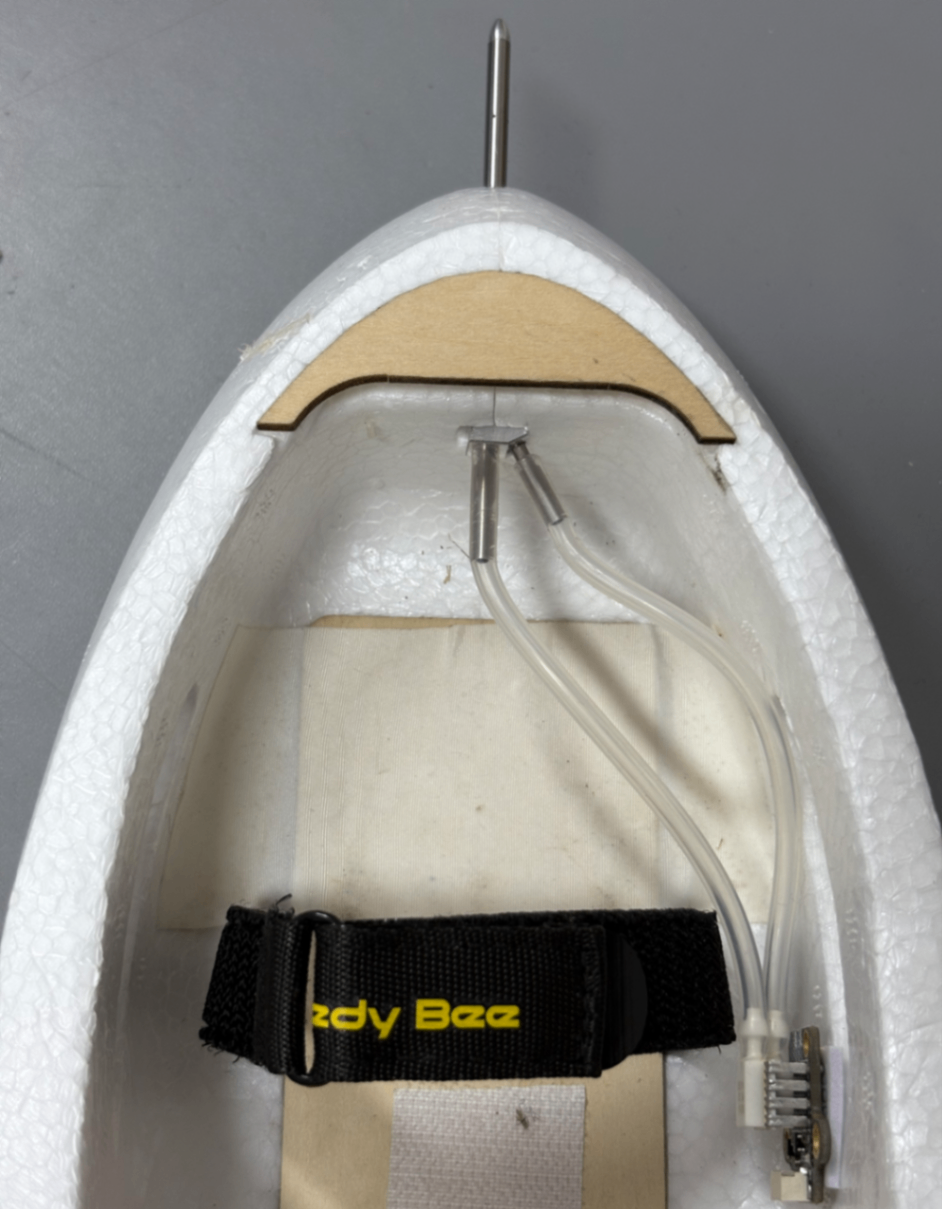

For detailed instructions on airspeed sensor installation, parameter configuration, and calibration, please refer to this article: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/airspeed/setup.html
V.Pre-Flight Checks and Calibration
5.1 ESC Calibration
⚠️ Ensure the battery is disconnected and propellers are removed!
① Go to the Output page
② Check the risk acknowledgment box
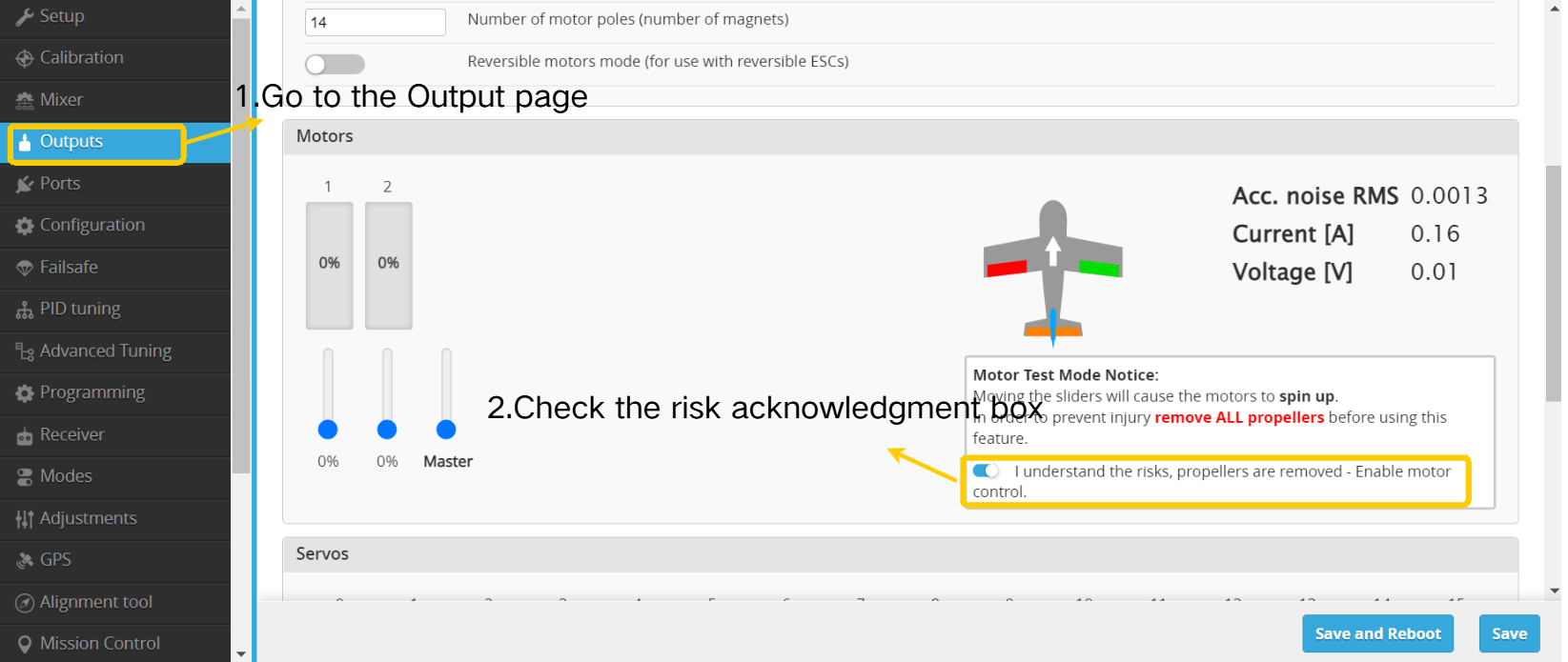
③ Immediately move the Master slider to 100%.
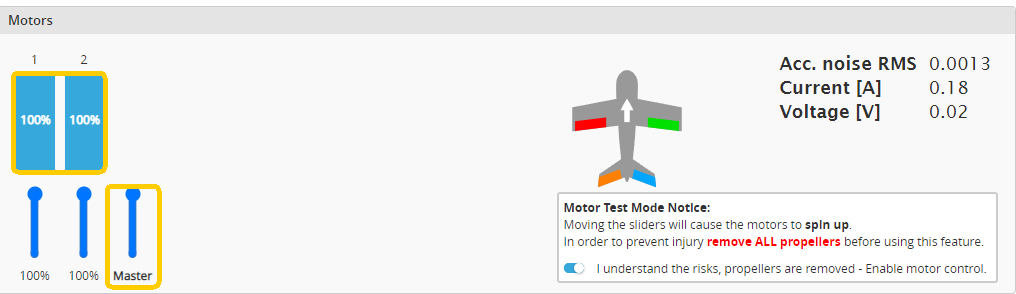
④ Connect the flight controller to the battery power.
⑤ After the ESC emits a confirmation tone, quickly move the Master slider to 0%; calibration tones will complete afterward.
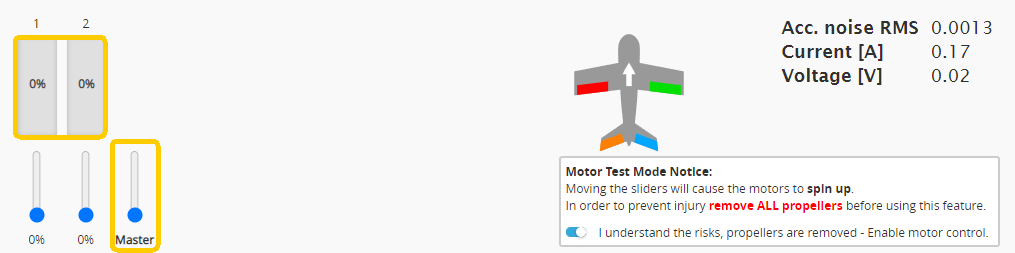
BLHeli32/BLHeli_S ESC Calibration Tones:
Connect battery, wait 2 seconds → ESC plays a musical tone indicating throttle high point → wait for tone to complete → move throttle to lowest position, wait 1 second → ESC plays another musical tone ("beep-beep") indicating throttle low point → calibration complete
PWM ESC Calibration Tones :
Connect battery, wait 2 seconds → ESC emits "beep-beep" indicating throttle high point → move throttle to lowest position, wait 1 second; ESC emits a series of short beeps indicating LiPo cell count → final "beep" confirms throttle low point → calibration complete
⑤ Slightly advance the throttle; the motor should immediately respond. Gradually move throttle from 0% to 20% to confirm linearity.
⑥ If the response is incorrect, disconnect the battery and return to step ② to recalibrate.
For enabling DShot protocol: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/esc/esc-calib-dshot.html
5.2 Motor Direction & Prop Installation
- Select standard or reverse propellers based on motor rotation direction.
- When installing propellers, ensure the printed side faces forward toward the airplane's nose.
If motor rotation direction is incorrect, swap any two of the three motor wires to correct the direction.

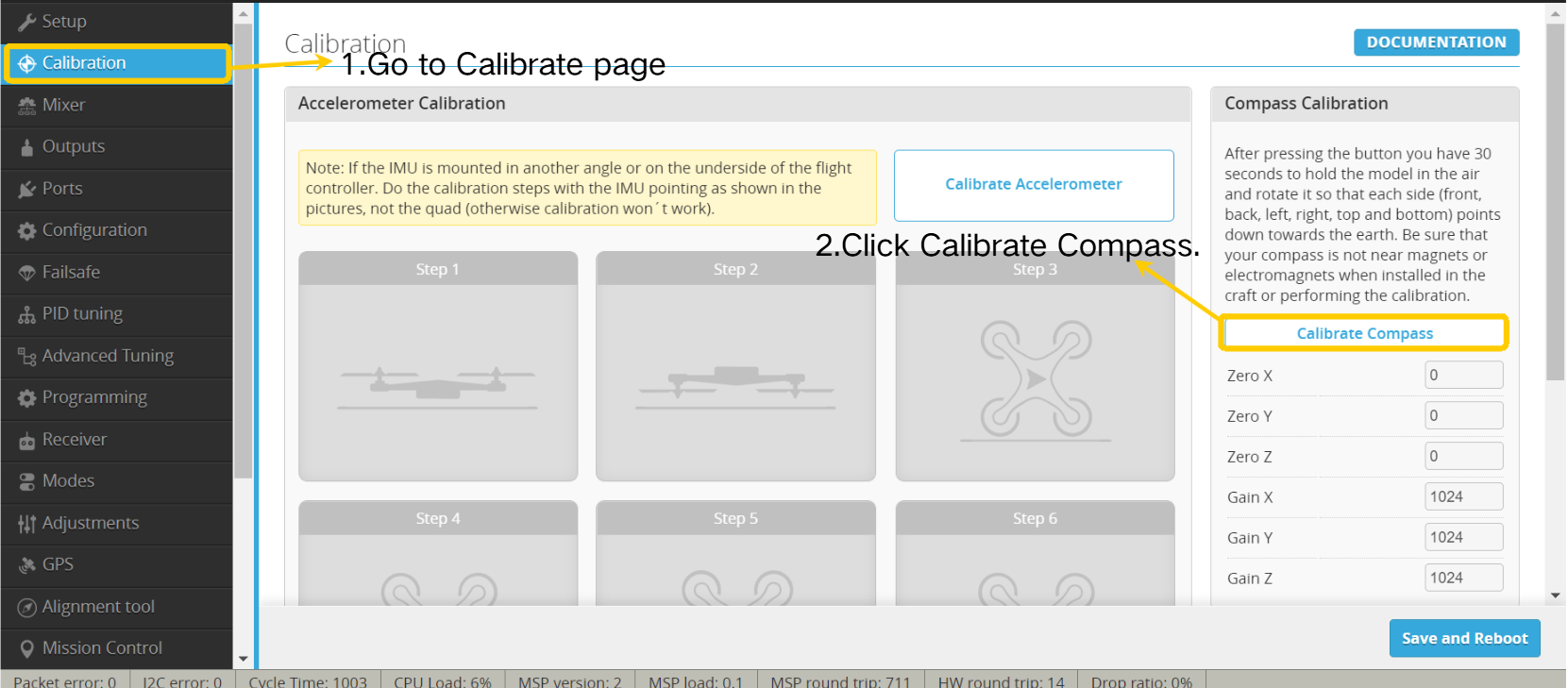
5.3 Compass Calibration
Before calibration, confirm the compass installation orientation!
- Enter the Configuration page.
- Select "Auto" to enable automatic detection, ensuring the compass is correctly recognized.
If the compass icon appears red, it means the compass is not recognized correctly. Please check the wiring or ensure the compass is working properly!
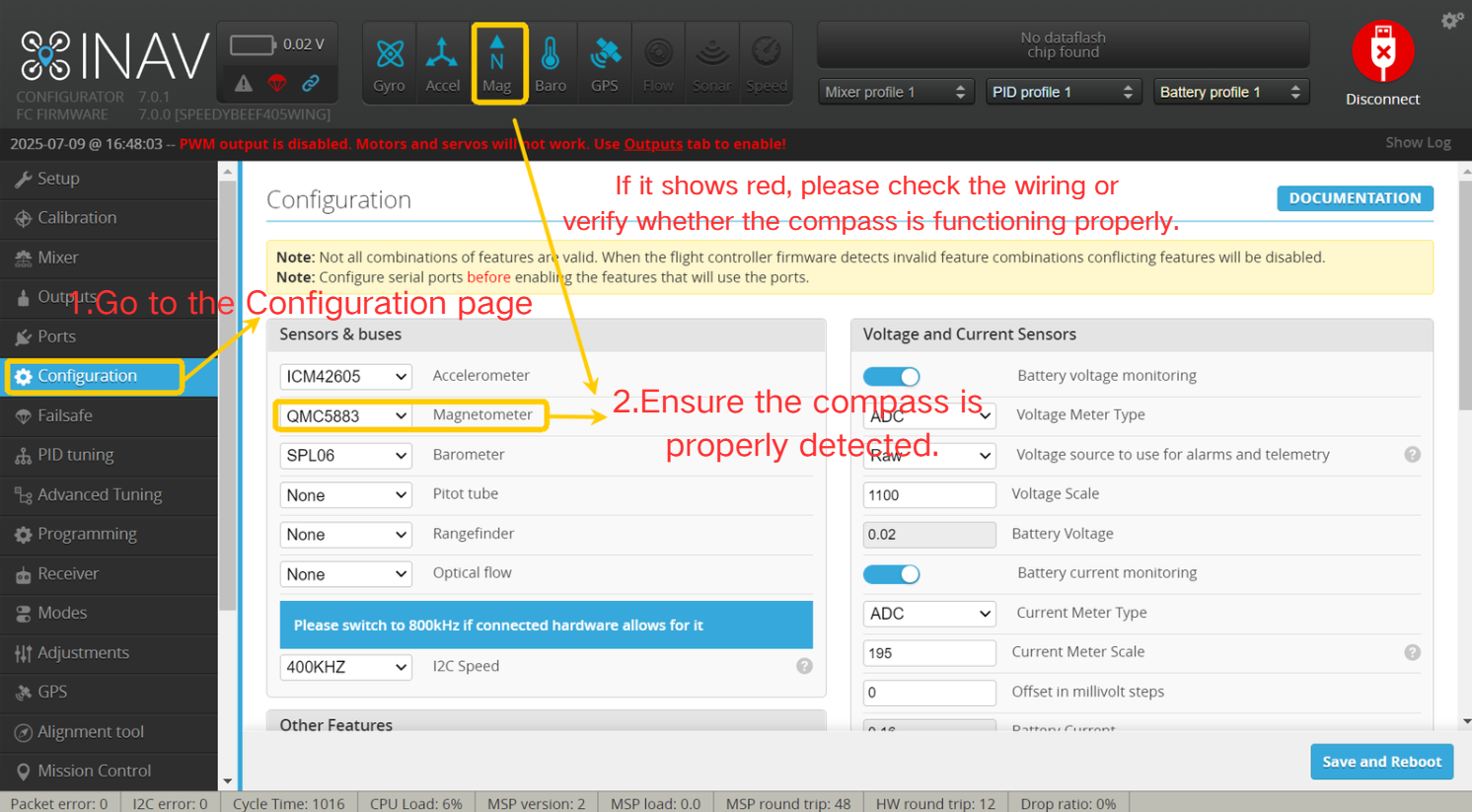
- Enter the Calibrate page.
- Click " Calibrate Compass”.
- Within 30 seconds, rotate the airplane 360° along each axis.
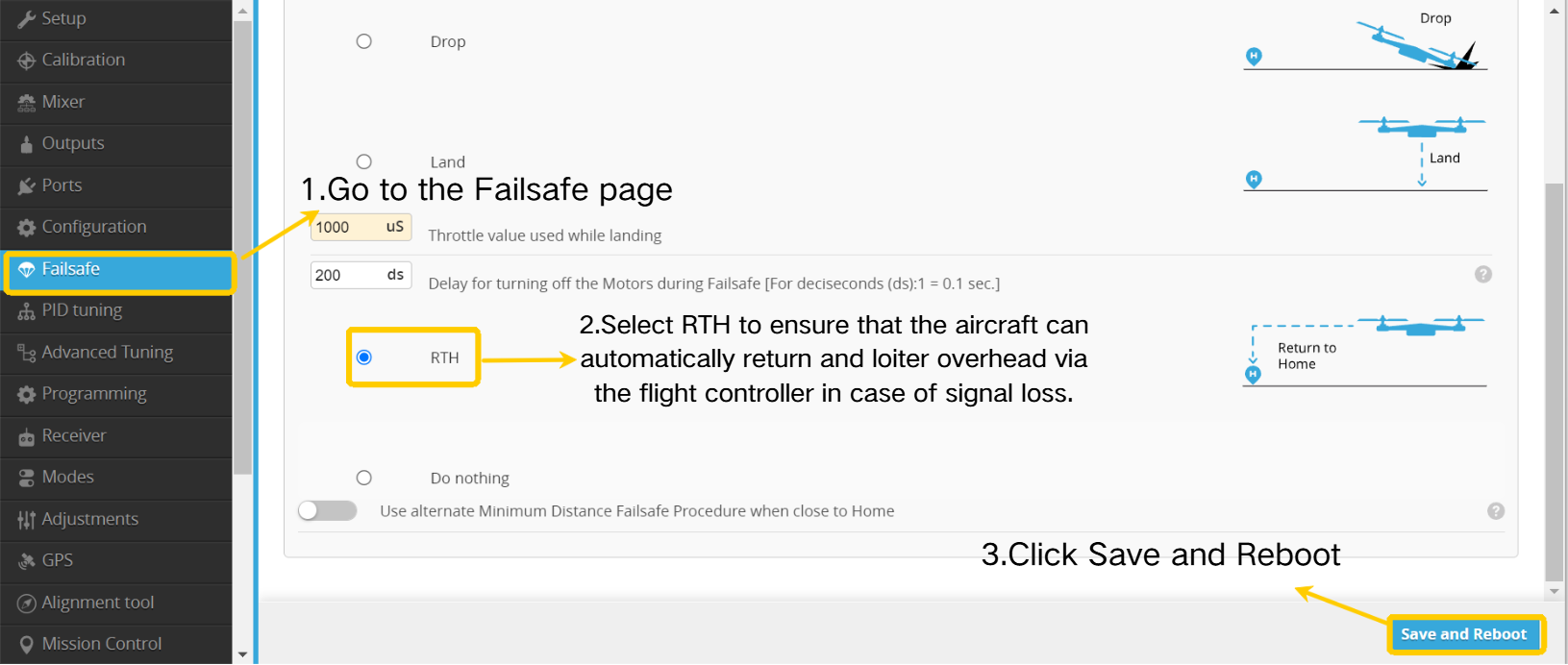
5.4 Failsafe Parameter Configuration
• Enter the Failsafe page.
• Select " RTH" to ensure the airplane autonomously returns and circles above the home point in case of signal loss.
• Click " Save and Reboot”.
- Click " Advanced Tuning”.
- Configure settings according to the illustrated guide.
- Ensure parameters highlighted within the red frame are set to " NEVER”.
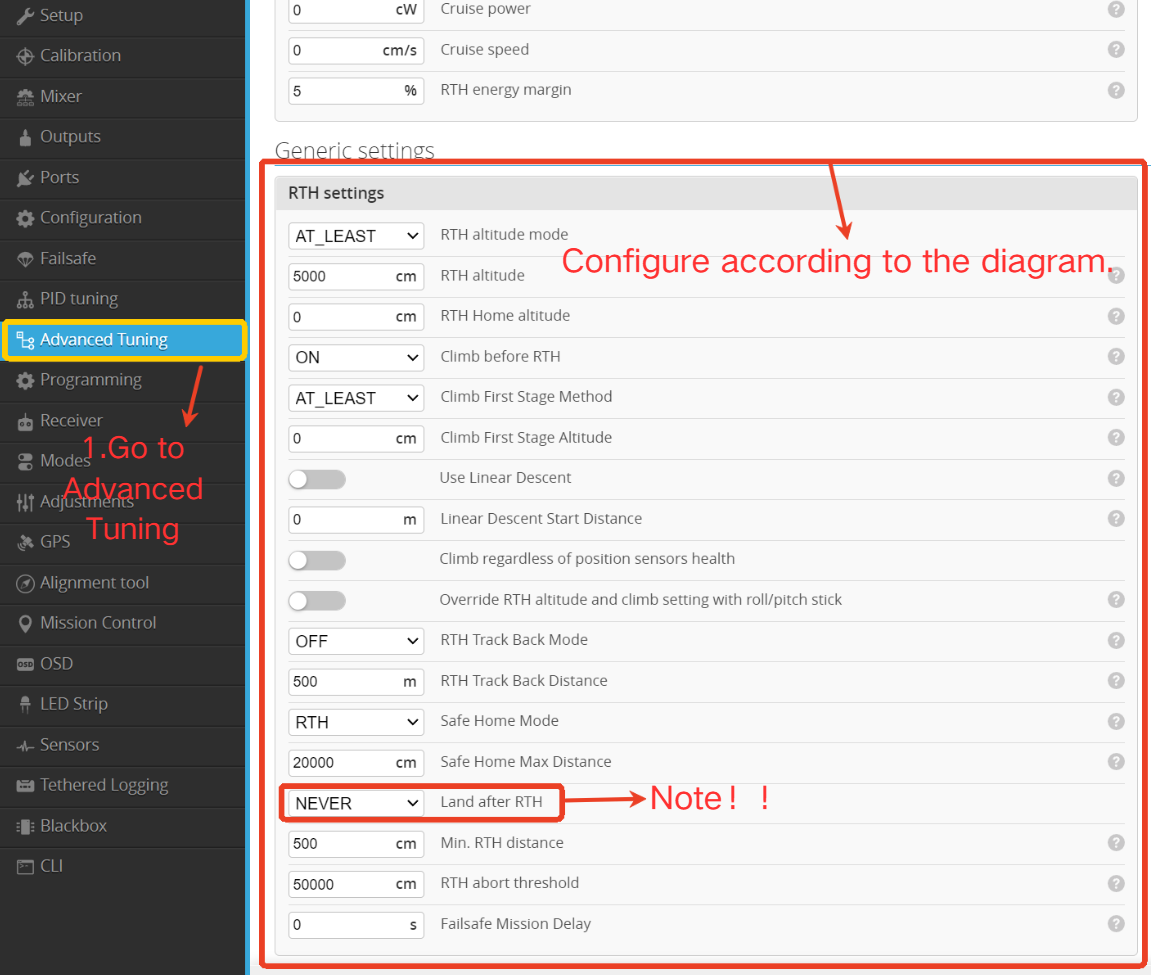
After completing the setup, make sure to click Save and Reboot to save the parameters.
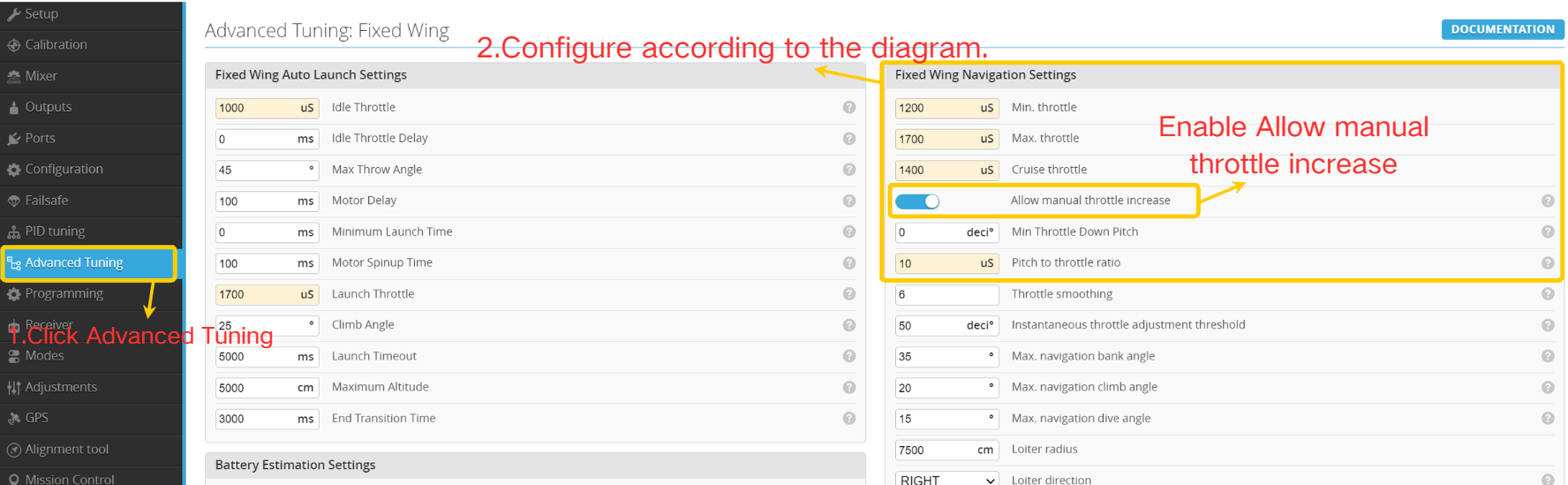
- Click " Advanced Tuning”.
- Follow the illustration to configure parameters, adjusting cruise throttle settings according to actual flight conditions.
- Click " Save and Reboot”.
During the initial RTH test flight, it is advisable to enter "Advanced Tuning" and allow manual throttle input to avoid overly low default return speeds, thereby preventing potential incidents.
VI. Flight Test
6.1 Pre-Flight Parameter Check
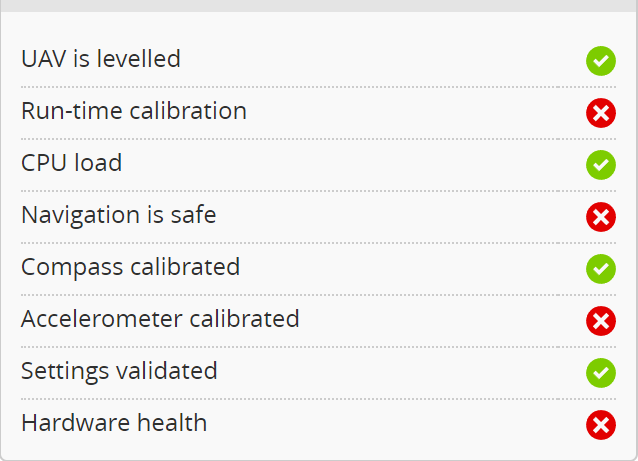
For common arming issues, refer to: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/fc/fcproblem/unlock-fail-common.html
6.2 Pre-Flight Checklist
6.2.1 Center of Gravity (CG) Check
1.Refer to the markings on the fuselage:
- The fuselage of a fixed-wing aircraft usually has markings indicating the recommended center of gravity(CG) , typically located 25–30% back from the leading edge of the main wing.
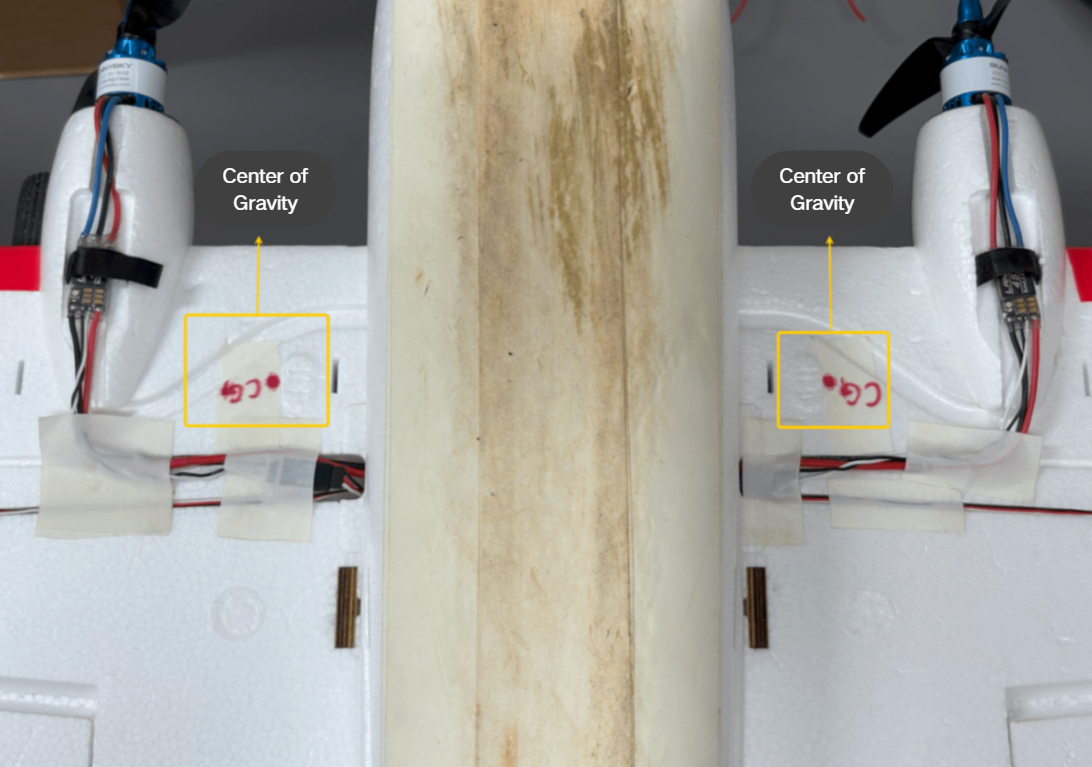
image.png
2. Finger Support Method:
- Place the aircraft on two fingers under the recommended CG point on the main wing and gently balance the fuselage
- If t he nose is too heav y or t he tail is too heavy, adjust the battery position or add/remove counterweight
Nose-Heavy (CG too far forward):
- The aircraft will have difficulty climbing during flight and may crash during takeoff
- Solution: Move the battery backward or reduce nose weight
Tail-Heavy (CG too far back):
- Airplane tends to pitch up easily, risking stalls.
- Solution: Move the battery forward or add weight to the nose
6.2.2 Control Surface Check Before Takeoff
Switch flight mode to ANGLE:
When the airplane rolls left, the left wing control surface moves downward, and the right wing control surface moves upward.
When the airplane rolls right, the left wing control surface moves upward, and the right wing control surface moves downward.
When the airplane pitches upward, the elevator moves downward.
When the airplane pitches downward, the elevator moves upward.
Switch flight mode to ACRO:
When moving the aileron stick left, confirm the left wing control surface moves upward, and the right wing control surface moves downward.
When moving the aileron stick right, confirm the left wing control surface moves downward, and the right wing control surface moves upward.
When pulling back on the elevator stick, the elevator control surface moves downward.
When pushing forward on the elevator stick, the elevator control surface moves upward.
When moving the rudder stick left, the rudder control surface moves to the left.
When moving the rudder stick right, the rudder control surface moves to the right.
6.2.3 GPS Satellite Count Check
When outdoors, check that the number of satellites is greater than 8—only then is it safe to take off!
If the satellite count stays below 8, move to a more open area. If the issue persists, consider replacing the GPS module.

6.2.4 Wind Direction Confirmation
Observe wind direction:
- Watch for visual cues like smoke, wind vanes, or flags,etc.
- Toss a light object (e.g., a blade of grass) into the air and observe the direction it drifts
Determine headwind takeoff direction:
- Taking off into the wind provides more lift and reduces the required takeoff speed
- Taking off downwind increases risk of stall or nose-down incidents, potentially causing crashes.
6.3 Takeoff Guidelines
Choose hand launch or rolling takeoff based on the actual aircraft configuration to ensure a smooth takeoff.
6.3.1 Hand Launch Takeoff
1. Mode preparation:
- Select ACRO mode to ensure full control surface authority
- Set throttle to 60%–80% to ensure sufficient takeoff thrust
2. Launch posture:
- Hold the airplane firmly beneath the wing; for flying wings, grasp the wing to prevent injury.
- Launch at an upward angle of approximately 30° to ensure sufficient lift.
3. Throwing technique:
- Use moderate force—avoid throwing too hard or too weak (which may not allow climbing)
- Push the aircraft forward smoothly, not downward
Important Notes:
Avoid hand launching at low throttle,ensure there is enough thrust for takeoff.
Immediately take control of the roll stick after release to prevent the aircraft from rolling out of control.
6.3.2 Rolling Takeoff
- Select ACRO mode
- Increase throttle to 60%–70% and maintain steady acceleration
- Keep the direction stable to avoid yaw deviation during rollout
- Once the aircraft reaches sufficient speed, gently pull up on the elevator to lift off smoothly
Important Notes: 1.Ensure the takeoff area is long enough—avoid steep climbs in short distances, which may cause stalls
2.Perform the takeoff into the wind to increase lift and reduce the impact of crosswinds
3.Monitor flight attitude to prevent excessive pitch-up or sharp banking
6.4 In-Flight Testing
1. Control Surface Test:
- After a successful takeoff, switch the flight mode to ANGLE and observe whether the aircraft automatically corrects its attitude
If the aircraft behaves abnormally, switch to ACRO mode to land, then inspect control surface behavior under ANGLE mode
2. Level Flight Test:
- Maintain throttle at 45%–55%, and check if the aircraft can fly level without diving or climbing
If the aircraft dives or climbs, recalibrate the horizontal level using AUTOLEVEL to ensure the flight controller is aligned with the wing
For detailed instructions on how to use AUTOLEVEL, refer to: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/fc/autolevel-autotune.html
AUTOLEVEL must be used in combination with a primary flight mode such as ANGLE. Refer to the AUTOTUNE setup section in the flight mode configuration for details on how to enable this combination.
3. Auto-Tuning:
- Switch the flight mode to AUTOTUNE to begin automatic tuning
For detailed instructions on how to use Auto-Tune, refer to: https://docs.speedybee.cn/plane/inav/settings/fc/autolevel-autotune.html
4. Flight Data Check:
- Monitor OSD data to verify that GPS, heading, altitude, ground speed, voltage, and current readings are all normal
If any data appears abnormal, land immediately and inspect the equipment
5. Return-to-Home (RTH) Function Test:
- Switch the flight mode to RTH and check whether the aircraft returns and loiters above the takeoff point
If the aircraft behaves erratically in RTH mode, immediately switch back to ACRO or ANGLE and review the RTH configuration parameters
6. Pre-Landing Check:
- Confirm there is enough remaining battery to complete landing
- Observe wind direction and choose to land against the wind for improved control and stability